Atoms Class 12 Notes Physics Chapter 12 - CBSE
Chapter : 12
What are Atoms ?
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gZIo1cSotkppzXCnH1rjDtQ92gnw7q8T/view
| Model | Important Points | Limitations |
| Alpha particle Scattering experiment |
|
|
| Rutherford’s Atomic Model |
|
|
| Bohr’s Atomic Model | Bohr incorporated following postulates in his theory: (i)The electron in an atom could revolve in certain stable orbits without the emission of radiant energy. (ii)The electron revolves around the nucleus only in those orbits for which angular momentum is some integral multiple of (h/2π) , where h is Planck constant ( = 6.6 × 10–34 Js) L = mvr = n(h/2π) where n = 1, 2, 3 and is called principal quantum number. (iii)Emission of radiation taken place when an electron makes a transition from a higher orbit to a lower orbit. During this transition, a photon is emitted having energy equal to the energy difference between the initial and final states hv = Ei – Ef |
|
| Topic/Term | Formula | Symbol Representation | Important Points |
| Rydberg formula for Spectrum of Hydrogen Atom | =(1/λ)=[(1/n2f)- (1/n2i)] | v= Wave number R = Rydberg constant = 1.097 × 107 m–1 ni = Initial state nF = Final state |
|
| Relation between Impact parameter (b) and scattering angle θ | b =(Ze2 cot(θ /2)/(4πε0K)) | Z = atomic number of the nucleous e = charge on electron θ = scattering angle K = kinetic energy of the α-particle i.e. (1/2)mv2 |
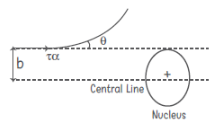 |
| Distance of closest approach (r0) | r0 =(Ze(2e)/4πε0 × K) | Z = atomic number e = charge on electron K = kinetic energy |
At the distance of closest approach whole of the kinetic energy the alpha particle is converted into potential energy. |
| Energy of hydrogen atoms | E = (-e2/8πε0r) | e = charge of electron | r = radius |
Share page on
Chapterwise Notes Class 12 Physics
- Electric Charges And Fields
- Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance
- Current Electricity
- Moving Charges And Magnetism
- Magnetism And Matter
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Alternating Current
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
- Wave Optics
- Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter
- Atoms
- Nuclei
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices And Simple Circuits
CBSE CLASS 12 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Accountancy Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Economics Notes
- CBSE Class 12 History Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Geography Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Political Science Notes
CBSE CLASS 12 SYLLABUS
- CBSE Class 12 English core Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Accountancy Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Economics Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 History Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Geography Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Political science Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Sociology Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Psychology Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Physical education Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Applied mathematics Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 History of Indian Arts Syllabus

