Sectors Of The Indian Economy Class 10 Notes Economics Chapter 2
What are Sectors of the Indian Economy ?
The dot mark ◉ field are mandatory, So please fill them in carefully
To download the complete Syllabus (PDF File), Please fill & submit the form below.
To download the complete Syllabus (PDF File), Please fill & submit the form below.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1mhT5r6u1-ccHBsCSBwsdOMJ7-YnXFiV0/view
Gross domestic productu
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) refers to the sum total of money value of all the production which has taken place in all these three sectors during a particular year. GDP shows the size of the economy
Unemployment
Unemployment is a very serious problem in India but bigger problem has been the underemployment. Underemployment is widely prevalent in primary sector. By right policies the government may tackle these problems in rural and urban areas. MGNREGA 2005 is helping the government a lot in tackling the problem of rural unemployment
Mgnrega 2005
- National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA) was formulated in 2005 and launched by the Prime Minister on 2nd February, 2006 Later on, its name changed to Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA).
- It targets Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs) and women suffering from poverty in the rural areas.
- It provides livelihood to the people below the poverty line. The scheme guarantees 100 days (recently amended to 150 days in drought-hit areas) of wage employment in a year to every rural household in 625 districts of the country.
- The Gram Panchayat, after proper verification, will register households and issue job cards to them.
- This Act is also called as Right to Work because if the government fails in its duty to provide employment, it will give unemployment allowances to the people. The type of work can be anything from road development, canal construction to any other similar work, which may increase productivity of the land.

| 1. Economic Activity: An economic activity is an act that is legal and creates utility with the objective of earning money. | 8. Underemployment: This is the situation in which people seem to be apparently working but all of them are made to work less than their potential. It is also called disguised unemployment. |
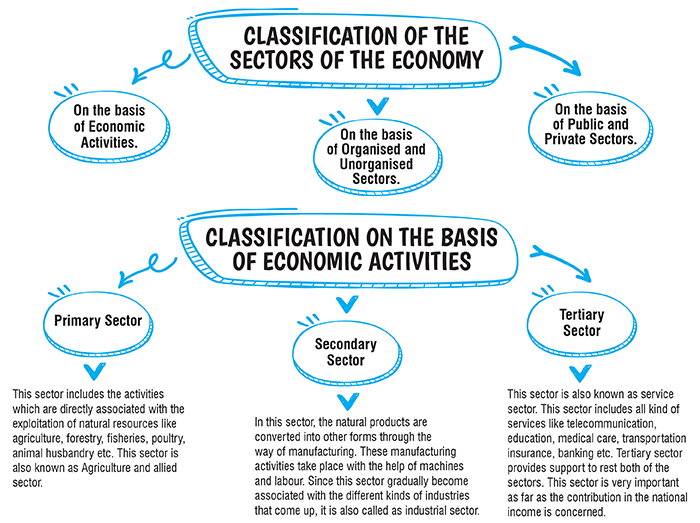
| 2. Primary Sector: This sector includes the activities which are directly associated with the exploitation of natural resources like agriculture, forestry, fishing and animal husbandry etc. | 9. Organised Sector: This sector includes the organisations which are properly registered with the government under various laws and the employment in this sector is regular and the organisations observe all the rules framed by the government for the welfare of the employees of the organisations. |
| 3. Secondary Sector: This includes the activities in which natural and other raw materials are converted into other forms with the help of machines. | 10. Unorganised Sector: This sector includes the organisations which are neither registered with the government nor observe any rule framed by the government for the welfare of the employees of the organisations. The employment in this sector is not regular and the terms of the employment are not written. |
| 4. Tertiary Sector: This sector includes all the services which helps in the operations of other two sectors as well. The services included are banking, transportation, communication, medical care, education etc. | 11. Public Sector: This sector includes the industrial organisations that are owned and operated by the government for providing goods and services to the people. The primary objective of this sector is the maximisation of welfare of the people. |
| 5. GDP: GDP or Gross Domestic Product refers to the market value of all the goods and services produced within the domestic territory in a year. | 12. Private Sector: This sector includes the industrial organisations that are owned and operated by the private entrepreneurs for providing goods and services to the people. The primary objective of this sector is the maximisation of profit for the organisations. |
| 6. Unemployment: It is a situation in which a person who is willing and able to work at the prevailing wage rate does not get any monetary work to do. | 13. MGNREGA: It is called Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act 2005 (MGNREGA 2005). Under MGNREGA 2005, all those who are able to, and are in need of work in rural areas are given guaranteed 100 days of employment in a year by the government. If the government fails in its duty to provide employment, it will give unemployment allowances to the people. |
| 7. Final Goods and Services: Final goods and services are those goods and services which have crossed all the stages of value addition and are available to be used by the final users. | |
