Control And Coordination Class 10 Notes Biology Science Chapter 7
To download the complete Syllabus (PDF File), Please fill & submit the form below.
Introduction
Living organims respond and react to their environment. The response to environmental factors (stimuli) such as light, heat, cold and pressure varies in different organisms. Plants bends towards light. Amoeba move towards food and tend to aggregate in moderate water. Unlike animals, plants do not have any special structures for perception of external stimuli.
Multicellular animals, except sponges have specialised cells called neurons for responding to stimuli. Neuron or nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of nervous system. Nervous system which includes the brain, spinal cord and nerves receives information from the surrounding, processes and interpret it and respond accordingly. The nervous system also passes information from one internal system to another. For example, smell or taste of food causes salivation.
Nervous system, therefore, controls and coordinates various functions in the body. The other organ system for control and coordination of various life processes is the endocrine or hormonal system. Plants are devoid of any nervous system or muscular system to coordinate and control their responses.
Tropism in Plants
Tropic movements in plants
Tropism is the response to stimuli that comes from one direction. If the movement of the plant part is towards the stimulus, then it is known as positive tropism. If the movement of the plant part is away from the stimulus, then it is known as negative tropism.
Types of tropisms
Phototropism
The growth movement in plants in response to light stimulus is known as phototropism. For example, the flower head of a sunflower is positively phototropic as it moves from East to West, along with the movement of the Sun. In the above activity, the shoots show positive phototropism, while the roots show negative phototropism.
Geotropism
The growth movement in plants in response to the force of gravity is known as geotropism. In geotropism, the roots of the plant always grow downwards, while the shoots always grow upwards, away from the earth.
Chemotropism
The growth movement in plants in response to chemical stimuli is known as chemotropism. For example, the growth of pollen tube towards the ovule in the ovary (through the stigma and style) is an example of positive chemotropism.
Hydrotropism
The growth movement in plants in response to water is known as hydrotropism. For example, the roots of some plants grow towards the water source, even when the water source is not present directly below it.
Thigmotropism
The growth movement in plants in response to a touch stimulus or contact with a solid object is known as thigmotropism. For example, in some plants, the coiling of tendrils occurs when they come in contact with objects for support.
Introduction of plant Hormones
Phytohormones
In plants, growth, development, and response to the environment is controlled and coordinated by a special class of chemical substances known as phytohormones. These hormones are produced in one part of the plant body and are translocated to other parts. For example, a hormone produced in the roots is translocated to other parts where they are required. Thus, the growth hormones of plants are known as phytohormones. These are naturally occurring organic substances. They are synthesized in minute quantities in one part of the plant body and are translocated to other parts where they are required.
Types of phytohormones
There are five major types of phytohormones: auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene. These phytohormones are either growth promoters such as auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, and ethylene, or growth inhibitors such as abscisic acid.
Auxins
When the growing parts of a phototropic plant detect sunlight, auxins (synthesized at the shoot tips) help the cells grow longer. When light falls on one side of the plant, the auxins generally diffuse towards the shaded side of the shoot. This stimulates the cells in the shaded area to grow longer than the corresponding cells of the illuminated region. This results in the curvature of the plant stem tip towards the light.
Gibberellins
They are produced in the roots of a plant. They promote stem elongation by promoting cell division in the inter-nodal region.
Cytokinins
They promote cell division. Therefore, they are present in greater concentration in those areas of the plants where rapid cell division occurs. For example, tip of the shoot. Abscisic acid It promotes seed dormancy by inhibiting cell growth. It is involved in the opening and closing of stomata. It is also responsible for the shedding of leaves.
Ethylene
It regulates fruit ripening. It is produced during the ripening of fruits.
Control And Cordination In Animal
Multicellular organisms have specialised organ system to coordinate their activities. Simple multicellular organism like Hydra consists of a network of nerve cells. Thus, Hydra has only nervous system to coordinate its activities. The control and coordination in higher animals (Human) takes place through combination of nervous system and hormonal system, i.e. neuro-endocrine system.
Animal Nervous System
In animal nervous system is highly evolved. The nervous co-ordination is brought about by the nervous system and the chemical co-ordination by hormones. Both the systems work in an integrated system.
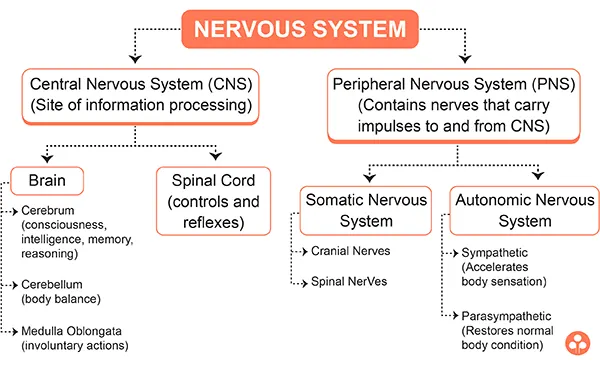
The Nervous system in Animal is divided into two main types .They are as follows
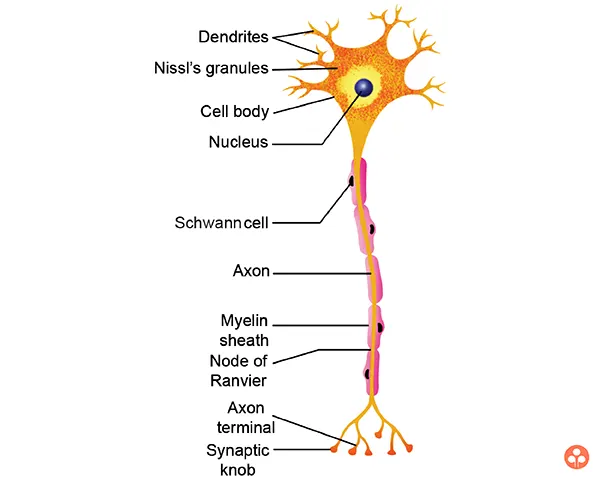
Neurons
The structural and Functional units of the vertebrate nervous system are neurons. These are specialised cells of different shapes and sizes in which the properties of irritability and conductivity have reached their maximum expression.
These respond to stimuli like light, electricity, chemical and mechanical agents, and transmit the excitations aroused by these stimuli to other neurons and to other cells of the body. Messages are conducted by nerves in the form of electrical impulses.
Structure of Neuron
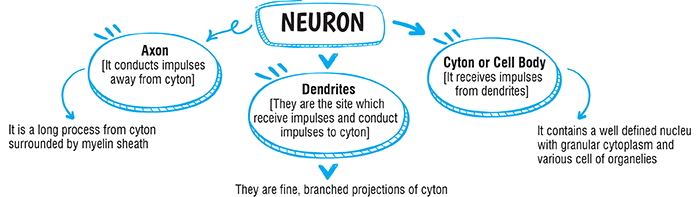
A nerve cell is an elongated cell which can be divided into 3 parts:
Dendrite
It is a hair-like process which is hollow. It is connected to the cyton. The number of dendrites may be more than one. Dendrites may also be branched. Dendrites receive sensation or stimulus which may be physical, chemical, mechanical or electrical. It passes on the stimulus to the cyton.
Cyton
This part of the neuron has a central nucleus and surrounding cytoplasm. Around the nucleus there are granules called Nissl granules. Stimulus is changed in cyton to another form called impulse. From one side of cyton arises a cylindrical process filled with cytoplasm. This process is called axon.
Axon
It is the longest part of the neuron. It transmits the impulse from cyton to the tip of the axon called axon bulb. The axon is generally covered by a sheath of lipoprotein called myelin sheath. This sheath is formed by a type of cell called Schwann cell. At one point the axon is slightly depressed (a notch, an indentation). This is called the node of ranvier. When an impulse travels along the axon, an electromechanical change can be seen.
Types of Nerves
There are three types of nerve fibres depending upon their function that in which direction they transmit the nerve impulse.
Sensory Nerves :
These receive sensory impulses from the receptor neurons and lie next to them. These are also called afferent nerves (Latin :afferent means carry toward). There nerves contain neurons which carry message (impulse) from sensory areas toward the central nervous system.
Motor Nerves :
These are final nerve cells that carry out the appropriate action in transmitting impulses to the effectors. These are also called efferent nerves (Latin :efferent means carry away).
These nerves contain neurons which take messages away from the central nervous system towards the effector organ, such as muscles and glands.
Mixed Nerves or Association neuron :
There are many nerves which are comprised of both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) nerve fibres. It interlink axon of sensory neuron and dendron of motor neuron. These are called mixed nerves. For example, most cranial and spinal nerves are called mixed nerves.
Functioning / Role of the nervous system
- All the nerve fibres carry messages in the form of nerve impulses.
- Excitability is an inherent property of nervous tissue and excitation does not remain at the site of its origin but is transmitted along nerve fibres. This properly of nervous tissue to transmit excitation is called conductivity.
- The nervous system receives a stimulus, through a receptor organ integrates or coordinates it, and effects a response through the effector organ. Thus, a coordinated behaviour has five main components – stimulus, receptor, coordinator, effector, and response.
- In such a coordinated behaviour, any stimulus of sound, sight, smell, etc. is perceived by receptor organs like eyes, ears, skin, etc.
- The brain and spinal cord are the coordinators which receives information in the form of messages called nerve impulses, from receptor organs via neurons. The information flows to the effector organs, i.e. muscles, and the response occurs.
- The passage of nerve impulse along a fibre involves a number of physical and chemical changes, none of which is directly visible.
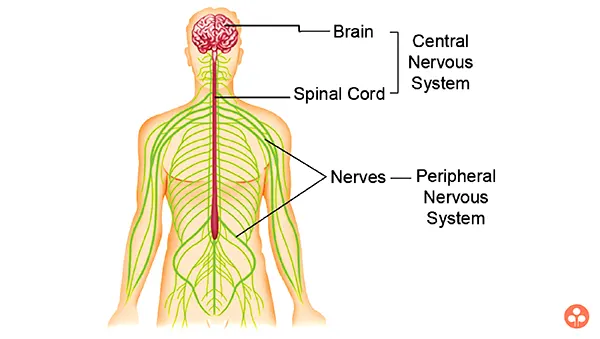
Central Nervous System
In vertebrates, the central nervous system consists of brain, and the spinal cord.
Brain:
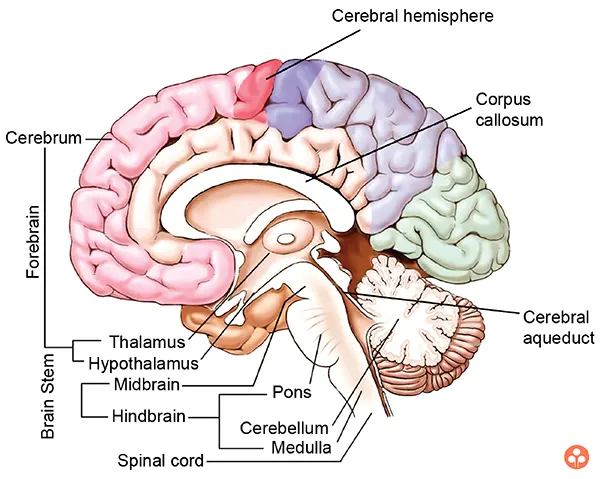
It is the most important organ which is lodged in the brain box, called cranium. Brain is covered by membranes called meninges. Between the membranes and the brain and also inside the brain, there is a characteristics fluid, called cerebrospinal fluid. The brain can be divided into three main parts:
(i) Fore-brain:
The forebrain consists of the Cerebrum, Thalamus and Hypothalamus.
The cerebrum is the biggest part of the brain. This part we associate with higher brain functions such as thinking and action. It contains the cerebral cortex and other subcortical structures. The cerebral cortex is highly wrinkled and makes the brain very efficient. Now the cerebral cortex again divides into four divisions called lobes.
They are:
- Frontal lobe –Is associated with parts of speech, reasoning, problem-solving, planning, movement and emotions
- Parietal lobe – We associate parietal lobe with recognition, orientation, and perception of stimuli
- Occipital lobe – Is responsible for visual processing
- Temporal lobe – Finally temporal lobe is associated with memory, speech perception and recognition of auditory stimuli
The cerebrum is divided into two halves by a deep furrow. These halves are the left and right hemispheres. Each side functions slightly different from the other, even though they are symmetrical. So the right hemisphere links to creativity whereas the left hemisphere relates to logic abilities. And Corpus callosum connects the two hemispheres.
(ii) Midbrain:
The midbrain connects the forebrain and the hindbrain. It acts as a bridge and transmits signals from hindbrain and forebrain. It is associated with motor control, vision, hearing, temperature regulation, alertness.
(iii) Hind-brain:
This is the posterior part which includes the cerebellum, the co-ordination centre of involuntary actions. Medulla oblongata is continued behind into the spinal cord.
Cerebellum: The cerebellum receives information from the sensory systems, the spinal cord and other parts of the brain and regulates the motor movements. It controls the voluntary movements such as posture, balance, coordination, and speech to maintain a smooth and balanced muscular activity.
Pons: It relays impulses between the lower cerebellum and spinal cord, and higher parts of the brain like the cerebrum and midbrain, also regulates respiration.
Medulla: Medulla directly controls many involuntary responses like sneezing and blinking of eye. It controls our overall major motor functions, or body movement. It carries out blood vessel dilation to increase or decrease oxygen flow and respond to heart function. Other functions include digestion, swallowing and vomiting to get rid of bacteria or pathogens that could harm us.
The brain is hollow. It has four longitudinal cavities called ventricles. In land vertebrates, 12 different cranial nerves are connected with the brain.
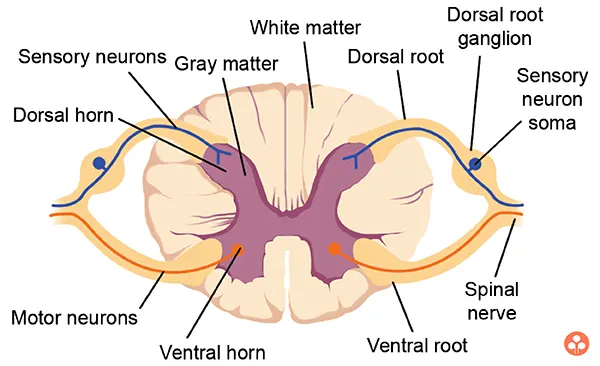
- It is a long cord which arises from medulla oblongata and runs all along the vertebral column. It pass through the neural canal which is a canal of vertebra.
- In the transverse section of a spinal cord, a central canal can be seen. This canal remains filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
- Immediately surrounding the canal, there are clusters of cytons which form the grey matter.
- In the peripheral part, axons are concentrated and, therefore, this area is called white matter.
- From each side of spinal cord, there are two horns, the dorsal horn and the ventral horn. To the dorsal horn joins a nerve which picks up sensation from the organ. It is called sensory organs.
- From the ventral horn or root arises the motor nerve which takes the message from the spinal cord to organ concerned. These two nerves constitute the reflex action. This action is very quick, for example, movements of eyelids, sneezing, coughing, yawning, hiccupping, shivering etc.
- In man 31 pairs of spinal nerves can be seen; eight in the neck region, 12 in chest region, five in abdominal region, five in hip region, and one in coccyx region. Coccyx is the last bone of the vertebral column.
Neuronswhat Is Reflex Action And Reflex Arc ?
When you touch a hot object or when a pin pricks your finger, what is your immediate reaction?
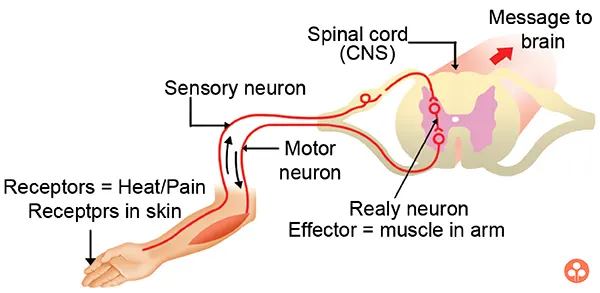
Of course, you remove your hand away from the source of pain, either the hot object or the pin. In situations like these, your reactions are always immediate, involuntary and sudden. They happen without much of a thinking process. In scientific terms, this action is called the reflex action. Here the spinal cord has a major role to play. The reflex arc shows the pathway through which the reflex action occurs.
Reflex Action
The whole mechanism of reflex action occurs in such a fashion that there is no conscious control of the brain. Stimulation occurs through the peripheral nervous system and the response to this peripheral nerve stimulation is involuntary. In a reflex action, the spinal cord along with the brain stem is responsible for the reflex movements.
A few examples of reflex action are:
- When light acts as a stimulus, the pupil of the eye changes in size.
- Sudden jerky withdrawal of hand or leg when pricked by a pin.
- Coughing or sneezing, because of irritants in the nasal passages.
- Knees jerk in response to a blow or someone stamping the leg.
- The sudden removal of the hand from a sharp object.
- Sudden blinking when an insect comes very near to the eyes.
The whole process of reflex action involves some important components. They are receptor organs, sensory neurons, nerve center, associated neurons, motor neurons and effector neurons.
The receptor organs perceive the stimuli. They are situated on the sense organs. The afferent neurons or the sensory neurons carry the stimuli from receptors to the spinal cord. The ganglion of the spinal cord has the sensory neurons.
The spinal cord is the nerve center, where synaptic connections are formed. The associated neurons are present in the spinal cord. The ventral horn of spinal cord has the motor neurons. Effector organs are the glands and muscles that behave in response to the stimuli.
Voluntary and Involuntary actions
Response is the activity of the body due to external or internal stimulus or a change in the environment. The response or actions that occur in the body can be of two types – voluntary and involuntary.
Voluntary Actions
Voluntary or conscious actions are the ones which we perform as per our wish. These are initiated by free will. For example, riding a bicycle, dancing, and eating an apple. These actions are controlled by the forebrain (cerebrum). The voluntary responses are slow as it take time to think (processing of the information) and to generate an impulse.
Involuntary or Reflex Actions
Involuntary or reflex actions are very sudden actions initiated by some stimulus such as pain, pressure, heat, cold, light or touch. Some examples of reflex actions include, withdrawing your hand on getting pricked, blinking of eyes and the dilation of the pupil.
Endocrine system
The endocrine system is a complex system made up of the endocrine gland which secretes a hormone or a stimulating hormone.
This finds the target organ and bind to the target receptors on it and brings about the required action. This forms the positive loop.
Sometimes, when there is excess or more than the required amount of the hormone in the bloodstream, a negative feedback is initiated to prevent further secretion of the hormone.
Hormone:
The term ‘hormone’ was introduced by Bayliss and Starling.
Hormones are the chemical messengers which coordinate the activities of living organisms.
The term hormone was proposed by Starling for those substances which are secreted by ductless gland in vertebrate bodies, which are capable of evoking response in the body.
Characteristics of Hormones:
- They are the secretions of endocrine glands.
- They are produced at a place and act on target organs which are mainly away from their source
- They are poured directly into the blood stream.
- They are required in very small quantities.
- They are specific in function.
- Chemically they are mainly proteins. Some of them may be amino acids, steroids etc.
- They are harmful if present in less or excess amounts.
- Hormones are immediately destroyed after their action is over.
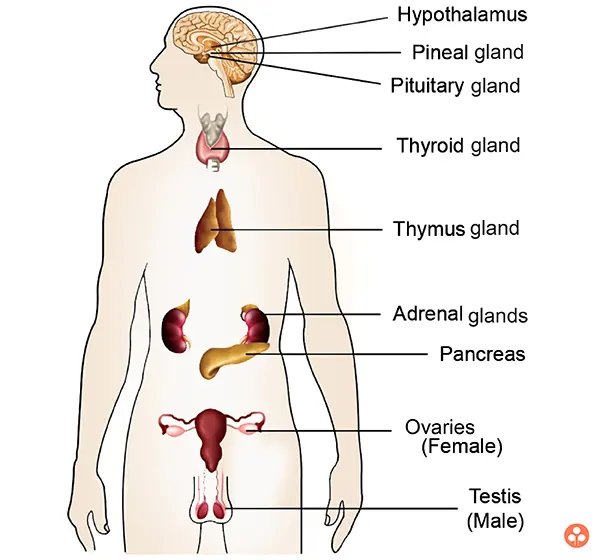
Endocrine Gland:
Endocrine glands are ductless glands which pour their secretions in the blood.
Various Endocrine Glands Present in the Human Body Are:
- Pituitary gland (or Hypophysis)
- Pineal gland
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid
- Thymus gland
- Adrenal gland
- Pancreas
- Ovaries
- Testes
Pituitary Gland (or Hypophysis):
The Pituitary glands is an ovoid slightly flattened body of tissue situated at the base of brain. It is red-grey in color attached to the hypothalamus of the brain by a stalk or infundibulum.
It is known as master endocrine gland because it regulates the activity of other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland consists of three lobes-the anterior lobe, the middle lobe and the posterior lobe.
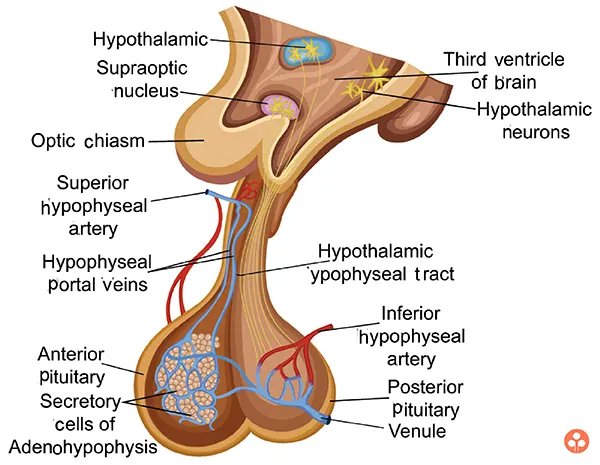
Hormones of anterior pituitary:
- Somatotrophin or Growth hormone (GH):
It stimulates growth and development of all tissues by accelerating protein synthesis and cell division, and by retaining calcium in the body. It also enables the cells to take up more amino acid and mobilise fat and makes the liver to release glucose for energy supply. - Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH):
This regulates the activity of adrenal cortex. It mainly stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete corticosteroid hormone which defends the human body under stress. - Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH):
This is also called Thyrotrophic hormone or thyrotropin. This stimulates growth of the thyroid gland and production of thyroid hormones. - Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH):It stimulates sperm formation in the male and growth of ovarian follicles in the female. In older persons, it helps to maintain sexual activity.
- Luteinising hormone (LTH):
In the male it induces the interstitial cells of the testes to produce male sex hormones namely androgens such as testosterone. This hormone makes the male genital system to become fully grown and functional. In the female, the luteininsing hormone causes ovulation, secretion of female sex hormones –Oestrogen from the maturing ovarian follicle, and progesterone by the corpus luteum transformed from the empty ovarian follicle. Follicle stimulating hormone and luetinising hormone are together referred to as gonadotrophic hormones or Gonadotropins. - Luteotrophic hormone (LTH):
This is also known as prolactin. This hormone stimulates growth of mammary glands during pregnancy and promotes lactation after delivery. Prolactin level rises during pregnancy and is very high during lactation.
Hormones of posterior pituitary:
- Vasopressin or Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): This causes the re-absorption of water into the blood from the collecting tubules of the kidneys, thereby concentrating the urine and reducing its volume.
- Oxytocin: This hormone stimulates uterus contractions at the time of child birth and causes release of milk from mammary glands. It is also known as birth hormone or milk ejecting hormone.
Pineal Gland: It is a small gland reddish-grey in colour, about the size of a pea, attached to the roof of the third ventricle of the brain. It contributes in regulating gonadal development. It controls development & concentration of melanin.
Thyroid Gland:
A gland that makes and stores hormones that help regulate the heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and the rate at which food is converted into energy. Thyroid hormones are essential for the function of every cell in the body. They help regulate growth and the rate of chemical reactions (metabolism) in the body. Thyroid hormones also help children grow and develop.
The thyroid gland is located in the lower part of the neck, below the Adam's apple, wrapped around the trachea(windpipe). It has the shape of a butterfly: two wings (lobes) attached to one another by a middle part.
Two hormones secreted by the thyroid gland are:
(i) Thyroxine: It is the principal hormone secreted by the thyroid gland and its main role is to increase the metabolic rate of the organs and tissues of the whole body. 60% of thyroxine consists of iodine, an element which is essential for the gland to enable it to synthesize its hormone. The basal metabolic rate (B.M.R.) is increased in hyperthyroidism and reduced in hypothyroidism.
(ii) Calcitonin: This hormone lowers the calcium level in two ways:
(a) By inhibiting renal tubular calcium re-absorption.
(b) By inhibiting bone calcium re-absorption.
Hypothyroidism: This results from lack or deficiency of thyroid hormone secretion. It is manifested differently in children as compared with adults. Cretinism affects children and is due to congenital defect of either absence or defect of the gland. In this disease growth is stunted, the features are coarse, frequently the child has a protruding tongue and an enlarged abdomen; the mentality of the child is low and retarded. Myxoedema is the condition caused by thyroid deficiency in adults. It affects women more frequently than men. It is characterized by puffy face, thick skin, dry cough, cold and loss of hair. There is a deposition of mucin and fluid retention in extracellular spaces. BMR is lowered Iodine deficiency causes simple goitre.
Hyperthyroidism : This results from excessive secretion and over action of thyroid hormones. An excessive amount of thyroxine is poured into the blood and the metabolism of the body is speeded up. The person starts losing weight, has an increased pulse rate, suffers from nervous excitement and there is protrusion of eye balls. These toxic signs and symptoms are responsible for the condition being known as toxic goitre. Other names are thyrotoxicosis, exophthalamic goitre and grave's disease.
Parathyroid Glands:
The parathyroid glands are usually four small rounded bodies of the size like peas which lie embedded in the dorsal surface of the thyroid gland.
They secrete Parathormone. It is released when there is low blood calcium level.
Parathormone maintains blood calcium and phosphate level by mobilising bone calcium into the blood and by pre preventing loss of calcium in urine.
Removal of glands results in the death of the individual within a week due to disturbances caused in the calcium metabolism, which leads to muscular tremors, cramps and convulsion, a condition called tetany.
Thymus Gland:
The thymus gland is an organ in the upper chest cavity that processes lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that fights infections in the body. This organ is part of both the lymphatic system, which makes up a major part of the immune system, and the endocrine system, which includes all glands that produce hormones. The thymus is most important in children and young adults, when it programs lymphocytes to attack antigens, like viruses. People who do not have this gland, or in whom it does not function correctly, usually have compromised immune systems and difficulty fighting disease.
Adrenal Glands:
These are two small semi-lunar structures lying one each on upper pole of the kidneys. That is why they are also known as supra renal glands.
Each gland consists of two structurally and physiologically separate parts known as cortex and medulla. The cortex occupies outer peripheral portion which is yellowish in colour and medulla is inner brownish part. Cortex secretes three different kinds of hormones known as corticosteroids. They are:
- Mineralocorticoids : These regulate sodium and potassium balance in the body.
- Glucocorticoids : These derive their name from their influence on carbohydrate metabolism. e.g. Glycogenesis is promoted in liver.
- Sex hormones: Small quantities of sex hormones as androgens and oestrogen are produced by adrenal glands which influence sexual development and growth.
- Adrenal medulla is important in raising defense mechanisms and supplementing sympathetic actions in the body. It secretes two hormones.
- Adrenaline: It is a stress hormone causes increase in systolic blood pressure, dilation of coronary blood vessels, increased sweating and increase in metabolic rate. It brings restlessness, muscle fatigue and anxiety.
- Noradrenaline: It is a general vasoconstrictor, increases both systolic and diastolic pressures. Both of these hormones are helpful in emergency conditions. Thus are called as "fight or flight response".
Pancreas:
The pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as an exocrine gland, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that pass to the small intestine. These enzymes help in the further breakdown of the carbohydrates, protein, and fat in the chyme.
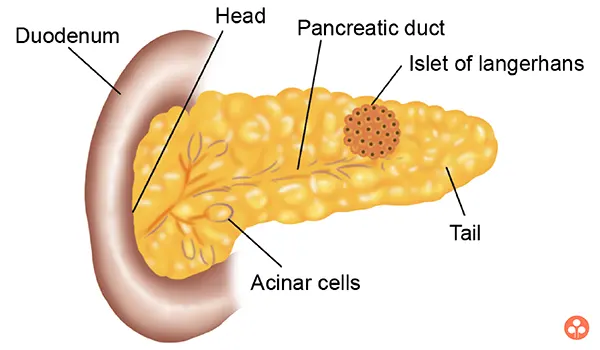
- Insulin is secreted by the beta cells and like other hormones, passes directly into the blood. Insulin is required to convert glucose into glycogen (glycogenesis) and store it in liver. Deficiency of insulin due to defect in islets of Langerhans results in diabetes mellitus, a condition in which blood glucose is high and is passed in the urine.
- The alpha cells of pancreas secrete glucagon, the metabolic effects of which are opposite to those of insulin. It causes the breakdown of liver glycogen, thereby releasing glucose into the blood stream.
- The third hormone somatostatin is secreted by the delta cells of the islets of Langerhans. It is able to inhibit the secretion of many hormones. As it inhibits the release of growth hormone of pituitary gland, it is also known as growth hormone release inhibiting hormone (GHRIH).
Ovaries:
Ovaries secrete three hormone:
- Oestrogen: FSH from the anterior pituitary controls the secretion of oestrogen by acting on the Graffian follicles. This hormone effects the development of female secondary sex characters. The oestrogen secretion influences the follicular phase. Its secretion is maximum during ovulation period. Moreover during pregnancy the oestrogen secretion by placenta keeps on increasing till full term.
- Progesterone: It is secreted by corpus luteum. This hormone in contrast to estrogen which is produced continuously during the reproductive years is secreted only after ovulation. Progesterone prepares the uterus for receiving the embryo. It prepares inner lining of the uterus .i.e. endometrium to receive the implanting embryo for about a week. If ovum gets fertilized, the corpus luteum continues to play a role in maintaining the pregnancy for the first three months, after which the placenta takes over the role of corpus luteum by secreting progesterone itself. This hormone is essential for the maintenance of pregnancy and is therefore called pregnancy hormone. If pregnancy does not follow ovulation, corpus luteum degenerates and breaks down due to the lack of progesterone.
- Relaxin : This hormone is secreted during later stages of pregnancy and leads to relaxation of muscles of the pelvic area to enable easy child birth and reduce the pressure on the foetus.
Testes:
Testosterone is the main testicular hormone secreted by interstitial cells of the testis. It is mainly concerned with the development and maintenance of male sex characters and enhancing the process of spermatogenesis.
What are Control and Coordination?
- Movements is one of the important characteristics of living beings.
- Changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli.
- Various organs or parts of the body of an organism works in a coordinated and proper manner to produce a reaction to the given stimulus which is called coordination.
- Nervous system and endocrine system are the two systems which play a major role in control and coordination.• Brain
Coordination in animals
Human Nervous SystemA
- Nervous system coordinates and controls all the voluntary and involuntary actions by transmitting nerve impulses to and from different parts of the body.
- Neuron is the structural and functional unit of nervous system.
- Synapse is a point of contact between axon terminals of one neuron with dendrites of another neuron separated by a minute gap.
- The terminals of axon have swollen ends which contain a chemical called acetylcholine – a kind of neurotransmitter.
- Brain is protected inside cranium of skull.
- Brain and spinal cord are protected by a three membranous layer called meninges.
- The three layers of meninges are Dura mater, Arachnoid, Pia mater.
- Space between covering membrane is filled with a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid which protects brain and spinal cord from shock or injury.
- Cerebrum of brain is divided into four lobes – Frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe and occipital lobe.
- There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves – 8 pairs in neck region, 12 pairs in thorax, 5 pairs in lumbar, 5 pairs in sacral and 1 pair in coccygeal region.
- Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system are antagonistic in functions.
- Spinal cord is the extension of medulla oblongata which runs through our vertebral column along the whole length of backbone.
- Reflex arc is the shortest route taken by an impulse from receptor to effector
- Stimulus → Receptors → Sensory neuron → Brain or Spinal cord → Motor neuron →Effector organ →Response.
- Cerebrum of brain is divided into four lobes – Frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe and occipital lobe.
- There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves – 8 pairs in neck region, 12 pairs in thorax, 5 pairs in lumbar, 5 pairs in sacral and 1 pair in coccygeal region.
- Hypothalamus secretes neurohormones and it also controls secretions of pituitary gland.
- The body has to maintain a normal state because too much or very less secretions of hormones is not good. If there is a rise in hormonal level the hormones secretion has to be reduced. Similarly if there is low hormonal level, its secretion has to be increased which is maintained by feedback mechanism.
Coordination in plants
- There are two types of movements : (i) Growth dependent movement. (ii) Growth independent movement.
- Curvature movements are changes in orientation of some plant parts in response to stimulus.
| 1. Tropic movements: These are directional movements of plant parts which involve growth in response to stimuli. | 8. Sensory neurons: Sensory neurons receive stimuli through their dendrites and transmit impulses towards central nervous system from receptors. |
| 2. Movements of curvature: These are changes in orientation of some plant parts in relation to others caused by external or internal stimuli. | 9. Motor neurons: Motor neurons transmit impulses from central nervous system to effectors. |
| 3. Nastic movements: These are non-directional induced variation movements that do not involve growth which occurs due to change in turgour pressure in response to stimuli. | 10. Receptors: Receptor is a sensory nerve cell or a group of sensory nerve cells which is sensitive to a specific stimulus or to a specific change in the environment. |
| 4. Hormones: Hormones are chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands which regulate various physiological processes in living organisms. | 11. Reflex actions: It is a spontaneous, quick, automatic response to a stimulus acting on a specific receptor without the will of an animal. |
| 5. Phytohormones: Phytohormones are naturally occurring organic chemical substances present in plants which control and coordinate various activities in them and are called as growth regulators. | 12. Reflex arc: It is the shortest route taken by a nerve impulse from receptor to effector during a reflex action. |
| 6. Coordination: The working together of various organs of the body of an organism in a proper manner to generate a proper reaction in response to a stimulus is called coordination. | 13. Cerebrospinal fluid: It is a clear, colourless, slightly alkaline fluid present in ventricles of brain, central canal of spinal cord and spaces between meninges which protects brain and spinal cord from injury and shocks. |
| 7. Stimuli: The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli. | 14. Endocrine glands: These are ductless glands which pour their secretion directly into blood stream and are carried by blood to the site of action or target organs. |