How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes Biology Science
Chapter 8
To download the complete Syllabus (PDF File), Please fill & submit the form below.
Introduction
All organisms produce offspring and thereby maintain their kind. The means by which organisms reproduce vary remarkably between species.
Reproduction is an orchestrated process. It needs the coordinated preparation of many tissues in female starting from maturation of ovum, its release its transportation, fertilisation and also the preparation of uterine wall to receive developing egg and its implantation.
The preparation for reproduction are cyclic in mammals. The change in structural and functional characteristics of both male and female reproductive tissue occur as a prelude to reproduce.
These are mediated by hormones. It is also concerned with the asexual development of the embryo from structures other than egg and also with the regeneration of lost or damaged parts and repair of defects.
Need of Reproduction: Reproduction is aimed at multiplication and perpetuation (stability) of the species. In other words it provides group immortality by replacing the dead individuals with new ones.
Basic Features of Reproduction: The modes of reproduction vary in different organisms. However all of these have certain common basic features. These are –
- replication of DNA
- cell division
- formation of reproductive bodies or units
- development of reproductive bodies into offsprings
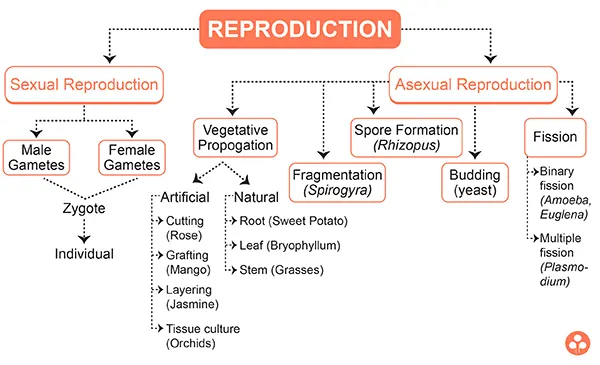
Production of offsprings by a single parent without the formation and fusion of gametes is called as asexual reproduction.
It is more primitive type of reproduction. It ensures rapid increase in number.
Characteristic
- It involves only one parent and no formation of gametes.
- The offspring produced is direct replica of the parent leaving no scope for variation.
- This is also called as vegetative or somatic reproduction and common in plants and lower animals
- Occurs by budding, binary fission, multiple fission, sporulation and also the regeneration.
- Protozoans, sponges and coelenterates reproduce mainly by this way.
Types Of Asexual Reproduction
(i) Fission:
It is the simplest form of reproduction in which unicellular organism either divides into two or many organisms.
It is also divided into two types:
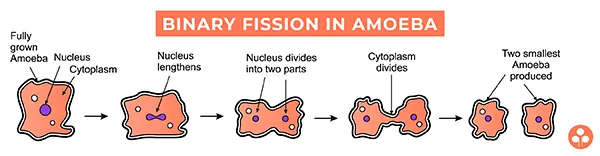
- Binary fission:
Binary fission, meaning "division in half", refers to a method of asexual reproduction. It is the most common form of reproduction in prokaryotes and occurs in some single-celled eukaryotes. After replicating its genetic material, the cell divides into two equal sized daughter cells. The genetic material is also equally partitioned, therefore, the daughter cells are genetically identical (unless a mutation occurred during replication) to each other and the parent cell. Transverse binary fission divides the cell across the short axis (e.g., most bacilli-shaped bacteria), longitudinal binary fission across the long axis (e.g.,Trypanosoma), and random binary fission across no defined axis (e.g.,Amoeba). Some biologist use this term for multi-cellular organisms that asexually reproduce by dividing into two (e.g., some star fish). This is also known as fragmentation. Spirogyra, a type of algae also reproduces by binary fission.
- Multiple fission:
Sometimes the nucleus divides several times, into many daughter nuclei. The daughter nuclei arrange at the periphery of the parent cell, and a bit of cytoplasm around each daughter nuclei is present. Nucleus develops an outer membrane. Finally the multi-nucleated body divides into many daughter cells. e.g. Plasmodium.

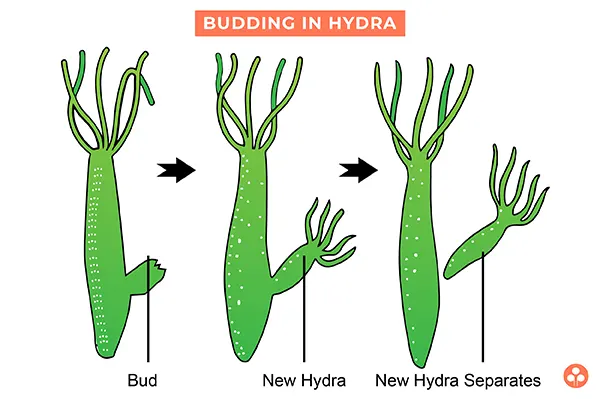
(ii) Budding: Formation of a daughter individual from a small projection which is called as bud, arising on the parent body is called as budding.
Budding is also of two types:
Exogenous budding: [External budding]
In this, bud arises from the surface of parent body. e.g., Hydra.
Budding in Hydra: A bulge appears on the body as a result of repeated mitotic division in the cells resulting in the formation of lateral out-growth called bud. This bud enlarges in size by further division of cells and attains the shape of parent. It then separates from the parent body and starts behaving as new Hydra.
Endogenous budding: [Internal budding]
In this, bud arises inside or within the parent body. e.g., Sponges.
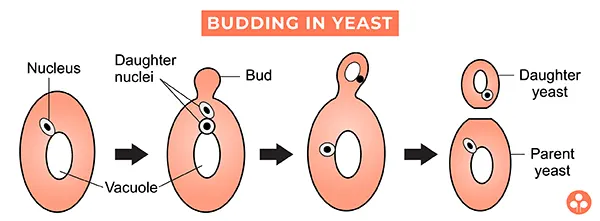
Budding in yeast: A small bud like out-growth appears at one end of the parent cell which gradually enlarges in size. The nucleus also enlarges and divides into two daughter nuclei. One nucleus remains in the parent cell and other goes to the daughter. When the bud attains almost similar size like parent, a constriction appears at the base of the bud separating it from the parent. However, sometimes a chain of buds can also be seen.
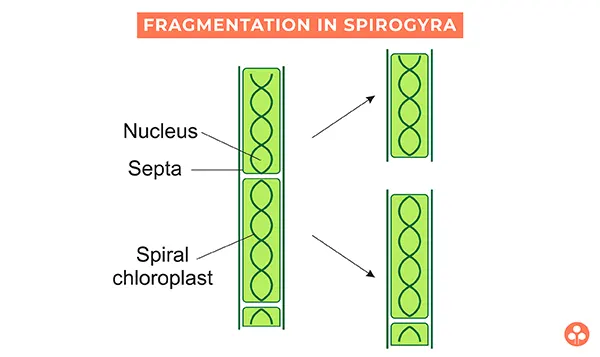
(iii)Fragmentation :
This is a type of asexual reproduction in fungi which is similar to the vegetative reproduction in some plants. In this process, a detached fragment of the fungal hyphae gives rise to a new individual under suitable conditions.
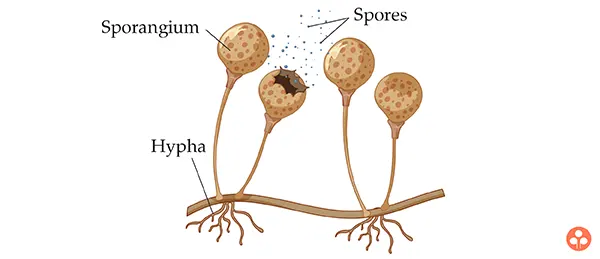
(iv) Sporulation :
In fungi, other than yeasts, the most common type of asexual reproduction is sporulation. The process of formation of spores is called sporulation. The spores formed in sporangia are called sporangiospores which are formed by several mitotic divisions. A sporangiospores germinate to develop into an organism with many vegetative hyphae.eg: Mucor
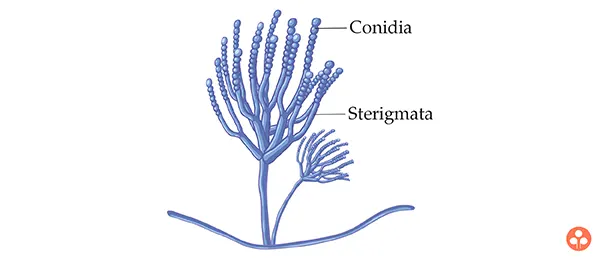
Conidia :
In this process the fungal hyphae differentiate into structures like sporangia, conidiophores etc., which will give rise spores or conidia by mitotic division. eg: Aspergillus
Spore formation:
A spore is a single or several-celled reproductive structure that detaches from the parent and gives rise, directly or indirectly to a new individual.
Spore formation takes place mostly in bacteria and fungi.
In fungi e.g. Rhizopus, Mucor, Aspergillus, Penicillium etc., spores are formed in a sac-like structure called sporangium at the tips of fungal hyphae. The nucleus divides inside the sporangium and gets surrounded by a small mass of cytoplasm forming a spore. After attaining maturity, the sporangial wall ruptures releasing the spores. The spores are covered with thick walls that protect them until they come in contact with another moist surface and can begin to grow.

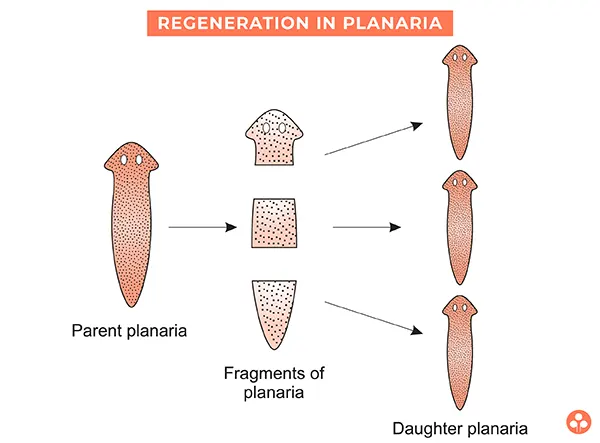
Regeneration
Regeneration is defined as a natural ability of some simple multicellular organisms to replace worn out parts, to repair damaged parts or to regrow cast off organs. It takes place mostly in Hydra, Planaria, sponges, etc. If sometimes the individual is somehow cut or broken into many pieces, many of these pieces grow into separate individuals. But regeneration is not same as reproduction since most organisms would not normally depend on being cut up to be able to reproduce.
Regeneration is performed by specialised cells. These specialised cells proliferate and make large number of cells. Different cells from the mass of cells undergo change to become various cell types and tissues. These changes takes place in an organized sequence referred to as development. Complex multicellular organisms cannot give rise to new individuals by regeneration. This is because they have complex body organization.
Vegetative propagation
Vegetative propagation: It is a form of asexual reproduction seen in plants. Plant undergoing vegetative reproduction propagates by a part of their body other than a seed. This part is called propagule. Vegetative reproduction is of different types.
Natural method: There are many plants which propagate naturally. Some plants propagate by roots e.g. sweet potato, guava, etc.; some by stems like ginger, banana, potato, strawberry; etc.; some by leaves like Bryophyllum, Begonia, etc.
Artificial method: There are some plants which propagates artificially by following methods :
Cutting: This is the very common method of vegetative propagation practised by the gardeners all over the world. It is the process in which a vegetative portion from plant is taken and is rooted in the soil to form a new plant. e.g. Grapes, Sugarcane etc.

Layering: In this process the development of adventitious roots is induced on a stem before it gets detached from parent plant, e.g., Mango, roses etc
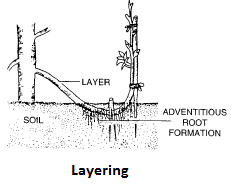
Mound layering: In the process of layering the lower stem branch of plant is used. Leaves are removed from this stem. Then it is bent close to the ground, pegged and covered with the moist soil in such a way that it's growing tip remains above the soil surface. This pegged down branch is called as layer. After a few days the covered portion of stem develops roots. This stem is then detached from the parent plant and is grown separately into a new individual. e.g. Jasmine
Air layering: It is adopted in those plants where stem cannot be bent to the ground. In this process the stem is girdled (i.e. ring of the bark is removed). Then it is covered with moist moss or cotton and wrapped with a polythene sheet to preserve the moisture. After few weeks adventitious roots develop from the injured part. The branch along with roots is then separated from the parent plant and planted to grow into a new plant. e.g. Orange, Pomegranate etc.
Grafting: The process of joining together of two different plants in such a manner that they live as one plants is called as grafting. Out of the two plants one is rooted in the soil and is known as the stock. The other part consists of a small shoot bearing one or more buds it is known as scion. Their union is carried out in such a way that their cambium must overlap each other. e.g. Mango, roses etc.

Methods of grafting.
There are four methods of grafting. They are
- Approach grafting
- Cleft grafting (or) Wedge grafting
- Tongue grafting
- Bud grafting
Approach grafting : Ex: Sapota, Mango, Guava etc.
- In this method both scion and stock remain rooted. A small slice is cut off from the stem of scion and stock.
- Scion is bent towards the stock. The two cut surfaces of the scion and stock are brought together and tied with a tape.
- In course of time the two stems get united. Then the top of the stock and the base of the scion are cut off.
Cleft grafting (or) wedge grafting
- The stem of the stock is cut across. A 'V' shaped insertion is made at the end of the stock.
- The scion is cut in shape. The scion is inserted into the 'V' shaped root stock. The point of union is held in position and a waxed tape is put around the junction.
Tongue grafting : This method is used on stocks that are relatively small.
- Top of the stock is cut diagonally and in an upward direction. Scion is cut diagonally in downward direction.
- A second cut is given from above downwards, which forms the tongue, such that the notch or tongue of the scion closely fits with that of stock.
- Union is tied with twine and covered with a waxed tape.
Bud grafting : Ex. Apple, orange, rose etc.
- A 'T' shaped incision is made on the bark of the stock.
- A bark is removed on either side of vertical cut.
- A single bud scion with a little wood is placed in the incision of below the bark and held in position applying tape.
Advantage of vegetative propagation.
- Vegetative propagation helps to maintain fixed qualities and characteristic features of the parent plant.
- For Example in ornamental plants with attractive flowers and leaves or any other interest in variation in one plant can be continued in next generation through vegetative propagation.
- Such plants can be produced in large numbers in a short time.
- Vegetative reproduction offers uniform root stock for budding or grafting.
- This root stock can be selected from a plant that is immune to diseases.
- In this method it would be possible to develop new varieties with useful characters.
- It can be used to grow other varieties by means of grafting.
- Vegetative propagation is a very useful method of reproduction in plants that rarely produce flowers.
Micro Propagation
Micro propagation: It has now become possible due to recent techniques to produce a large number of plantlets from a small piece of tissue taken from the shoot tip or other suitable plant parts. This method of propagation is called as micro-propagation. It involves the process of tissue culture. e.g., Orchids. ornamental plants etc.

Mechanism of micro propagation:
- A small piece of plant tissue placed in a culture medium divides rapidly to form a shapeless lump called ‘callus’.
- The callus is then placed in different culture media to stimulate the development of root and shoot.
- Tiny plantlets are formed from just few cells which are transplanted into pots or soil where they can grow to form mature plants.
Advantages of micro propagation
- It is a fast technique producing many plantlets from a small plant tissue in few weeks and using very little space. In other words, it is quite economical.
- The plants produced by tissue culture are disease free.
Sexual Reproduction In A Flowering Plant
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants involves transformation of diploid sporophytic cells into haploid gametophytic cells by meiosis and subsequent fusion of haploid gametes of opposite sex to form diploid zygote. The zygote then develops into an embryo which ultimately forms a diploid plant body. In flowering plants, all these steps of sexual reproduction occur within specialized reproductive organs, called the flowers.
Structure of the flower: Morphologically flower is a modified shoot meant for sexual reproduction of the plant. Typically, it is a condensed branch in which internodes have become condensed, bringing nodes very close to one another, and the leaves are modified to form floral whorl that directly or indirectly participate in the process of reproduction.
The flower is commonly borne on short or long stalk called the pedicel. It has an upper swollen region known as receptacle (thalamus or torus).
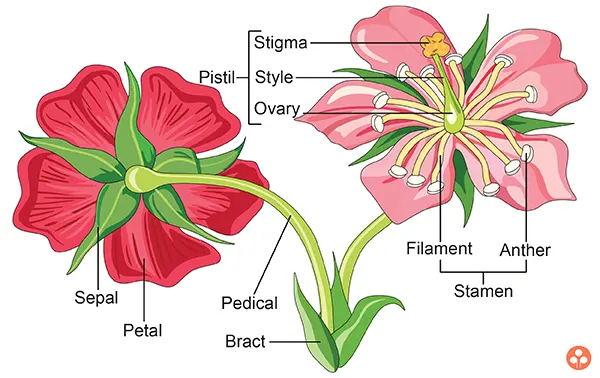
Parts of a flower: A typical angiospermic flower consists of four whorls of floral appendages attached on the receptacle : calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium. Of these, the two lower whorls (i.e., calyx and corolla) are sterile and considered as nonessential, accessory or helping whorls. The two upper whorls (i.e., androecium and gynoecium) are fertile and considered as essential or reproductive whorls.
- Calyx : It is the outermost whorl of the flower. It is composed of leaf like green sepals. The sepals are essentially green in colour but in some cases they are coloured like petals. Such a condition of calyx is called petaloid. Sepals enclose the bud and protect the delicate part within. They prevent rapid transpiration from the inner parts of the flower.
- Corolla :This is the second whorl of the flower and consists of a number of petals. Petals are generally brightly coloured and sometimes fragrant which make the flower to become attractive. Petals usually attract the insect pollinators and helps in pollination. The petals and sepals together form the floral envelope called perianth
- Androecium : It is the third whorl of flower and is the male reproductive organ consisting of stamens. Each stamen is made of filament and anther. The filament supports anther at its tip. Usually anthers are bilobed and contain four microsporangia (or pollen sacs), but sometimes they have only one lobe and two microsporangia. The portion of stamen which connects the anther and the filament is known as connective.
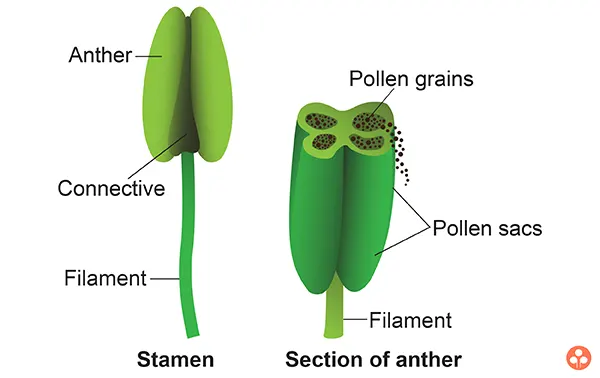
(A) Filament: It forms the stalk that bears more or less cylindrical or ovoid anther.
(B) Connective: it connects anther to filament.
(C) Anther: It is present on the top of filament. Each anther consists of two lobes that is why it is called as bi-lobed. Each anther lobe has two pollen sacs which contain millions of tiny microscopic pollen grains, called as microspores. The pollen grains are like yellow dusty powder in appearance.
- Gynoecium :This is the last and the fourth whorl of flower and is the female reproductive organ of the flower. It occupies the central position on the receptacle and composed of ovary, style and stigma and the component parts are called carpels.Ovary encloses the ovules. Stigma is the receptive spots which lodges the pollen grains. Style is the connection between stigma and ovary.
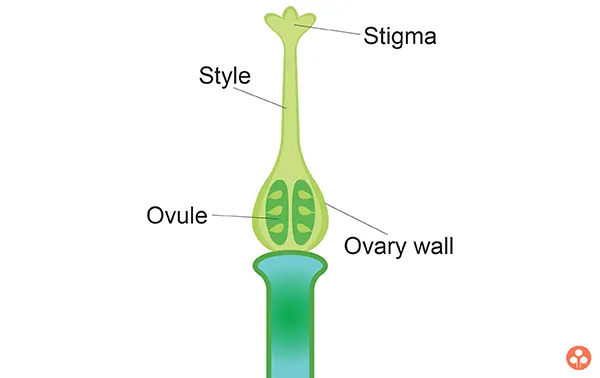
Each pistil usually consists of three distinct parts - ovary, style and stigma.
- Ovary: It is a basal, swollen part of the pistil. The ovary has one or more chambers called the loculi which are distributed in a special cushion like parenchymatous tissue called the placenta, from which the ovule develops.
- Style: From the top of the ovary arises a long, elongated structure called as style.
- Stigma: The terminal end of style is called as stigma. It is rough, hairy or sticky to hold pollen grains during pollination process.
Types of flower based on reproductive organs
- Unisexual: In such flower, only one reproductive part is present, either male (stamen) or female (pistil) e.g. cucurbits, mulberry, papaya, watermelon, etc.
- Bisexual: When stamens and carpel are found in the same flower, it is called hermaphrodite or bisexual, e.g. Hibiscus (china rose), mustard, rose, pea, cotton, etc.
Pollination
The process of transfer of pollen grains, from an anther to the stigma of the same flower or of different flower.
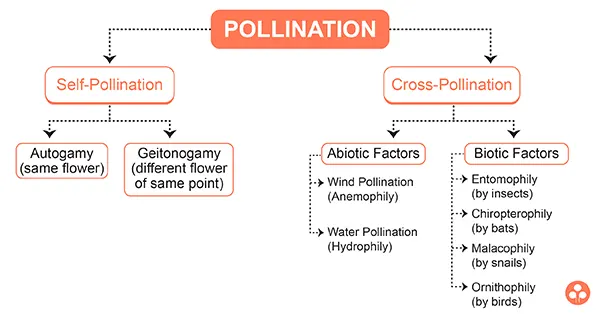
It is of two types :
- Self pollination
- Cross pollination
- Self pollination :This process involves the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers to the stigma of the same flower or of another flower borne by the same plant. It is of two types :
- Autogamy :It is a kind of pollination in which the pollen from the anthers of a flower are transferred to the stigma of the same flower.
- Geitonogamy :It is an kind of pollination in which the pollen from the anthers of one flower are transferred to the stigma of another flower borne on the same plant. It usually occurs in plants which show monoecious condition (unisexual, male and female flowers are borne on the same plant). Geitonogamy involves two flowers but these belong to the same parent plant.
Merits
(a) Pollen grains are not wasted.
(b) The purity of the generation is maintained.Demerits
(a) New and healthier varieties are not formed.
(b) It results in weaker progeny, producing weaker seeds and plants.Contrivances for self pollination :The major contrivances or adaptations which favours self pollination are :
- Bisexuality :Flowers should be bisexual or hermophrodite.
- Homogamy :Anthers and stigma of the bisexual flowers of some plants mature at the same time. They are brought close to each other by growth, bending or folding to ensure self pollination. This condition is called homogamy. e.g., Mirabilis (Four O, clock), Catharanthus (Vinca), Potato, Sunflower, Wheat, Rice, etc.
- Cleistogamy :Some plants never open to ensure complete self-pollination. This condition is called cleistogamy, e.g., Commelina bengalensis, Oxalis, Viola, etc. The cleistogamous flowers are bisexual small, inconspicious, colourless and do not secrete nectar.
- Cross pollination :Cross pollination involves the transfer of pollen grains from the flower of one plant to the stigma of the flower of another plant. It is also called xenogamy.
Merits
(a) Seeds are more and viable
(b) Progenies are healthier.
(c) Adaptability is better.
(d) New varieties can be produced.Demerits
(a) The process is not definite because plants depend on agencies.
(b) Large amount of pollen grains are wasted.
Contrivances for cross pollination: Nature favours cross pollination. All unisexual flowers and a large number of bisexual flowers are naturally cross pollinated.
The main contrivances ensuring cross pollination are as follows :
- Diclincy or Unisexuality: In unisexual flowers stamens and carpels are found in different flowers. Unisexuality can be of two types :
- Monoecious plant : When male and female flowers are borne on the same plant. e.g., Maize, Cucurbits, Castor.
- Dioecious plant: When male and female flowers are borne on different plants. e.g., Carica papaya, Cannabis.
- Dichogamy: In bisexual flowers, when two sexes mature at different intervals and thus avoid self pollination is known as dichogamy. When stamens mature earlier than the stigma, it is known as protandry and the flowers are called protandrouse.g. Coriander, Jasmine, Sunflower, Lady’s finger, etc. When stigma matures earlier than the stamens, it is known as protogynyand the flowers are called protogynous. e.g., Rose, Tobacco, Crucifers, etc.
- Heterostyly: The plants of some species in which flowers are dimorphic. Thus, facilitate cross pollination. Some of them possess a long style but short stamens and are known as pin-eyed while others have short style and long stamens. These are known as thrum-eyed. e.g., Oxalis.
- Herkogamy :In some bisexual flowers where the stigma and anthers mature at the same time, self pollination is avoided by some sort of barrier. The flowers show following contrivances :
- The male and female sex organs lie at some distance from each other.
- In some flowers corolla has peculiar forms which act as barrier in self pollination. e.g. sAristolochia.
- In some other flowers, the pollens are held together to form pollinia which can only be carried away by insects. e.g. Orchids and Calotropis.
- Self sterility or Incompatibility : When pollen grain of an anther do not germinate on the stigma of the same flower, then such flower is called self sterile or incompatibility and this condition of flower is called self sterility, intraspecific incompatibility or self incompatibility. In these flowers cross pollination is the only means for fertilisation and production of seeds.
- Agents for cross pollination :Cross pollination involves external agents for the transfer of pollen grains of one flower to the stigma of another flower. There are two main groups of agents :
- Abiotic agents like wind and water
- Biotic agents which include animals of different types such as insects, birds, bats, snails, etc.
- Abiotic agents
- Anemophily :When flowers are pollinated by wind agency, the phenomenon is known as anemophily. Wind pollinated flowers produce very large amount of pollen grains to compensate the wastage. Pollen grains of such plants are small, light, dry, and smooth. The female flowers have large feathery or brush like stigmas to catch the pollen grains. Anemophilous flowers are small and inconspicuous with long and versatile stamens. e.g. Sugarcane, Maize, Wheat, Bamboo, Pinus, Papaya, Grasses, Typha, Datepalm, Coconut, Mulberry, Chenopodium, etc. This type of pollination mainly observed in Graminae
- Hydrophily :When the pollination takes place through the agency of water, it is known as hydrophily. All aquatic plants are not hydrophilous some are anemophilouse.g.Potamogeton, Myriophyllum or Entomophilous .eg. Alisma, Lotus. Hydrophily is of two types :
- Hypohydrophily :Plants which are pollinated inside the water e.g.Zostera, Ceratophyllum, Najas, etc.
- Epihydrophily :Plants which are pollinated outside the water. e.g.Vallisneria (Ribbon weed).
- Biotic agents
- Entomophily : When pollination is brought about by the agency of insects, it is known as entomophily or insect pollination. About 80% pollination occurs by insects like moths, bettles, butterflies, wasp, etc. All the flowers pollinated by insects are brightly coloured, have a sweet smell and produce nectar. Entomophilous flowers produce a small amount of pollen which has a spinous and sticky exine due to presence of pollenkitt. The stigmas of such flowers are long rough and sticky. The insects visit the flower for nectar, edible pollen grain and shelter. Bees obtain both nectar and pollen grains from the flowers and have basket for collecting pollen. Salvia is excellent example of insect pollination is which pollination occurs by lever or turn pipe mechanism. Other examples of insect plants A Flower pollinated by Honey bee and Butterfly.
- Abiotic agents
- Entomophily : When pollination is brought about by the agency of insects, it is known as entomophily or insect pollination. About 80% pollination occurs by insects like moths, bettles, butterflies, wasp, etc. All the flowers pollinated by insects are brightly coloured, have a sweet smell and produce nectar. Entomophilous flowers produce a small amount of pollen which has a spinous and sticky exine due to presence of pollenkitt. The stigmas of such flowers are long rough and sticky. The insects visit the flower for nectar, edible pollen grain and shelter. Bees obtain both nectar and pollen grains from the flowers and have basket for collecting pollen. Salvia is excellent example of insect pollination is which pollination occurs by lever or turn pipe mechanism. Other examples of insect plants A Flower pollinated by Honey bee and Butterfly.
- Chiropterophily : It is a mode of pollination performed by bats. The flowers they visit are large, dull-coloured and have a strong scent. Chiropterophilous flowers produce abundant pollen grains. These flowers secrete more nector than ornithophilous flowers and open at night emit a good fragrance. e.g.Kigeliapinnata (Sausage tree), Adansonia (Baobab tree), Bauhinia megalandra, Anthocephalus (Kadam tree), etc.
- Malacophily : Pollination by slugs and snails is called malacophily. Land plants like Chrysanthemum and water plant like lemna shows malacophily. Arisaema (aroid; snake plant) is often visited by snails.
- Malacophily : Pollination by slugs and snails is called malacophily. Land plants like Chrysanthemum and water plant like lemna shows malacophily. Arisaema (aroid; snake plant) is often visited by snails.
Fertilisation In Plants
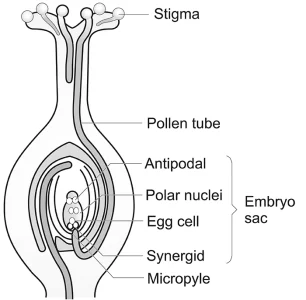
Fertilisation: The fusion of male gamete with the female gamete to form a diploid zygote within the embryo sac is called fertilisation.
Mechanism of fertilisation
- Due to pollination the related pollen grains are deposited over the receptive stigma of the carpel.
- These pollen grains absorb water, swell and then germinate to produce pollen tubes.
- The pollen tube grows into the stigma, passes through the style and then moves towards the ovarian cavity.
- Two male gametes are formed inside the tube during its growth through the style.
- After reaching the ovary, the pollen tube enters the ovule with its tip piercing the egg apparatus.
- The tip of the pollen tube ruptures releasing two male gametes into the embryo sac.
- One male gamete fertilises the egg to form the diploid zygote by the process of syngamy.
- The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei to form the triploid (3n), primary endosperm. This is known as triple fusion. The mechanism involving two acts of fertilisation in an embryo sac is called double fertilisation.
Formation of fruits and seeds
- The fertilised egg divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule.
- The ovule then develops a tough coat around it which gradually gets converted into a seed.
- All the fertilised eggs in the ovules present in an ovary grow to become seed.
- The ovary of the flower develops and becomes a fruit, which may be soft like mangoes; juicy like oranges; hard, dry and woody like peanuts and almonds.
- The petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off.
- The fruit protects the seed. The seed is the reproductive unit of a plant. It contains the baby plant.
- The part of the baby plant that develops into shoot is called plumule and the part which develops into root is called radicle.
- The part of the seed which contains stored food for the baby plant is called cotyledon.
- The baby plant inside the seed develops into a seedling under suitable conditions like water, air, temperature, etc. This is called germination.
Differences Between Self Pollination And Cross Polination:
| S.No. | Self Pollination | Cross Pollination |
| 1. | Pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower (autogamy) or another flower borne on the same plant (geitonogamy). | Pollen grains are transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower borne on a different plant of the same species (allogamy). |
| 2 | Both the anther and stigma mature at the same time. | The anther and stigma of a flower generally mature at different times |
| 3. | It can occur even when the flowers are closed. | It occurs only where the flowers are open. |
| 4. | External agent is not required for self-pollination. | An external agent abiotic or biotic, is essential for cross-pollination |
| 5. | It is economical for the plant. | Cross-pollination is not economical as the nectar, scent and bright-coloured corollas, etc. |
| 6. | Self-pollination ultimately results in progenies which are pure lines i.e. homozygous. | Cross pollination produces the offsprings which are hybrids I.e., heterozygous. They show variations in characteristics. |
| 7. | It cannot eliminate useless or harmful characters. | It can eliminate useless or harmful characters. |
| 8. | Highly useful characters get preserved in the race | Useful characters cannot be preserved in the progenies. |
| 9. | Self-pollination does not introduce any variations and hence the offsprings are unable to adapt to the changed environment. | Cross−Pollination Introduce variations in the offsprings These variations make these plants to adapt better to the changed environment or the struggle for existence. |
| 10. | Immunity of the race towards disease falls in the succeeding progenies. | Immunity of the race towards disease is usually maintained in the succeeding progenies. |
| 11. | Yield of the plant gradually falls with time. | Yield of plant usually does not fall |
| 12. | Self-pollination never helps in the production of new varieties and species. | Cross-pollination is a mechanism of producing new varieties and species among plants. |
Reproduction In Human Beings
The reproductive organs in human beings become functional after attaining sexual maturity. In males, sexual maturity is attained at a age of 13 – 14 years. In females, it is attained at an age of 12 – 13 years. This age is known as the age of puberty. During sexual maturity, hormonal changes take place in males and females, and under the influence of these hormones secondary sexual characteristics are developed.
Secondary sexual characteristics in males include deepening of voice, widening of shoulders, appearance of beard and moustaches, growth of axillary and pubic hair, enlargement of external genital organs and formation of sperms.
Secondary sexual characteristics in females include growth of axillary and pubic hair, widening of pelvis and hip, enlargement of breasts and initiation of the menstrual cycle.
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system consists of the two following organs – a pair of testes, a pair of epididymis, a pair of vasa deferentia, urethra, penis and accessary glands.
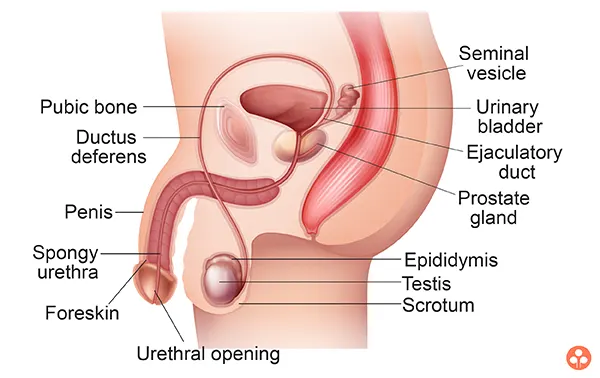
Male reproductive system comprises of following parts:
- Testes
- Scrotum
- Vasa efferentia
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Ejaculatory duct
- Urethra
- Accessory sex glands
- Penis
Testes:
Testes are one pair of small sized oval shaped 4 to 5 cm long, pinkish coloured primary sex organ of male. These are present in a thin pouch made up of skin and connective tissue called scrotal sac or scrotum hanging from lower abdominal wall between the leg. Scrotal sac acts as thermoregulator and it keep the testicular temperature 2°C lower than body temperature. This temperature is suitable for development of sperms. Each testis is externally covered by a white fibrous capsule, the tunica albuginea which is produced inside the testis as fibrous septa. The septa divide the testes into a number of testicular lobes. Each lobule has one to three convoluted seminiferous tubules. The combined length of all seminiferous tubules is about 200–400 metres. Between the seminiferous tubules connective tissue are found. In this connective tissue interstitial cells also called Leydig cells are present as clumps. These cells secrete the male sex hormone, testosterone. This hormone regulates the maintenance of primary and secondary sexual charateristics in males.
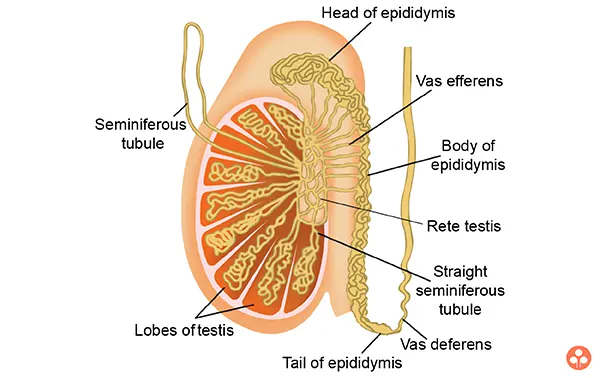
Epididymis
- Epididymis is very coiled long tube of 6m. It is commonly known as store house of sperms.
- Storage and activation of sperms take place here. Its secretion also contributes to seminal fluid. Sperm can be seen for 10 Hr. to 10 days in it.
- If there is no ejaculation for longer time the sperms get absorbed by its wall.
Vasa deffrentia
- Each epididymis continues from its lower end as a vas deferens.
- It enters into abdominal cavity through inguinal canal, forms loop round the uretor and joins the duct of a seminal vesicles to form an ejaculatory duct. The ejaculatory duct opens into the urethra.
- Near its end the vasa deferens is enlarged to form a spindle like ampulla for the temporary storage of sperm.
- It is cut or tied off as the birth-control measure called vasectomy.
Urethra
It arises from the urinary bladder and joins the ejaculatory duct to form urinogenital canal as it carries urine, sperm and secretion of seminal vesicles prostrate and cowper’s gland.
Urethra is 20 cm long, passes through the penis and it is differentiated into prostatic part (2.5 cm) membranous part (2.5 cm) and penile part (15.0 cm). Finally it opens at tip of penis.
In male it is the common pathway for release of urine and seminal fluid.
Penis: It is a long and thick muscular organ made up of mostly erectile tissue. It opens outside the body. It passes the sperms from the man’s body into the vagina of the women’s body during mating.
Accessory sex glands
Seminal vesicles: These are elongated coiled sacs. They secrete seminal fluid that contains sugar fructose. It provides energy to the spermatozoa.
Prostate gland: This gland surrounds the first portion of urethra. It secretes a fluid containing citrate and enzymes that nourish and activates the spermatozoa that swim.
Semen
- Sperms and secretion of accesory glands collectively known as seminal fluid or semen.
- It is milky, semi-solid in nature having particular smell.
- pH – 7.35 – 7.5, specific gravity – 1.028
- The Semen has many functions as –
- Provide fluid medium to sperms
- Nourish and activate sperms.
- Facilitate the sexual act by lubricating the reproduction tract of the female.
Spermatozoa
- Human sperm lives for many weeks in gonoduct but, once ejaculated it survives only for 24 to 48 hrs.
- The sperms are released in millions. In one ejaculation about 200,000,000 (2 × 108) sperms are discharged. Sperm move with the speed of 2 mm/minute in female tract.
- Structurally, a human sperm has three main parts – head, neck and tail. The tip of a sperm is covered by a cap-like structure, acrosome, which helps the sperm to penetrate inside the egg during fertilisation.
Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system is designed to carry out several functions. It produces the female egg cells necessary for reproduction, called the ova or oocytes. The system is designed to transport the ova to the site of fertilisation. Conception, the fertilisation of an egg by a sperm, normally occurs in the fallopian tubes. The next step for the fertilised egg is to implant into the walls of the uterus, beginning the initial stages of pregnancy. If fertilisation and/or implantation does not take place, the system is designed to menstruate (the monthly shedding of the uterine lining). In addition, the female reproductive system produces female sex hormones that maintains the reproductive cycle.
It is more complex as compared to that of males. It consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina.
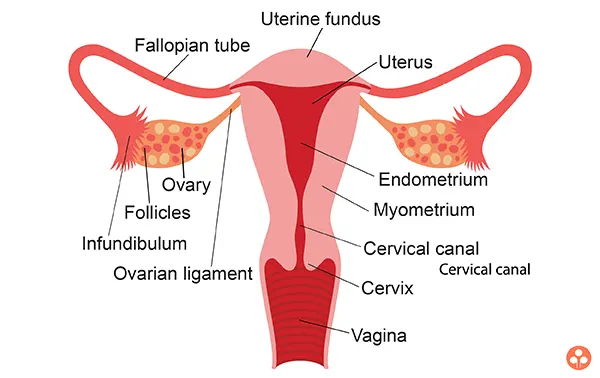
Ovaries: They are the primary sex organs located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity near kidney. Each ovary is connected by a ligament to the uterus. It produces gametes (eggs) and hormones like estrogen and progesterone. Ovary is composed of ovarian follicles. Each follicle contains a large ovum (egg) surrounded by many layers of follicle cells.
When a girl is born, the ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs. At puberty some of these eggs start maturing. One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries. The release of egg from the ovary is called ovulation. It is caused by increase in turgidity aided by contraction of unstriped muscle fibres around the follicles. The force of ejection carries the egg to the fallopian tube. In women each measures about 3 cm × 2 cm × 1 cm and surrounded by the fold of peritoneum.
Ovaries produce ova and secrete female sex hormones, oestrogen and progesterone. The process of formation of egg in the ovary is known as oogenesis.
Fallopian tubes: These are narrow tubes that are attached to the upper part of the uterus and serve as tunnels for the ova (egg cells) to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. Conception, the fertilization of an egg by a sperm, normally occurs in the fallopian tubes. The fertilized egg then moves to the uterus, where it implants into the lining of the uterine wall.
Uterus (womb):It is a large (8 cm × 5 cm × 2 cm) hollow muscular, highly vascular and pear shaped structure present is the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. It is formed of three parts :
- Fundus :It is upper dome shaped part above the opening of fallopian tubes.
- Body or corpus :It is middle and main part of uterus. Its wall is formed of outer peritoneal layer called perimetrium; middle muscular mucosa or myometrium of smooth muscle fibres and inner highly vascular and glandular mucosa or endometrium.
- Cervix : It is lower narrow and of uterus that connects the uterus to the vagina, which leads to the outside of the body.
- Vagina: The vagina is a large, median elastic muscular tube. It is adapted to receive the male penis during copulation. The vagina is also called “birth canal”. It allows the passage of baby at the time of child birth.
Gland:
- Bartholin's gland: It secretes a clear, viscous fluid under sexual excitement.
- The fluid serves as a lubricant during copulation or mating.
Menstrual Cycle
- It is a cyclic phase of the flow of blood with mucus and tissues etc. from the uterus of a woman at monthly intervals.
- It occurs on average of 28 days interval.
- It starts at the age of 12-14 years and stops at 45 - 50 years of life.
- This cycle stops during pregnancy.
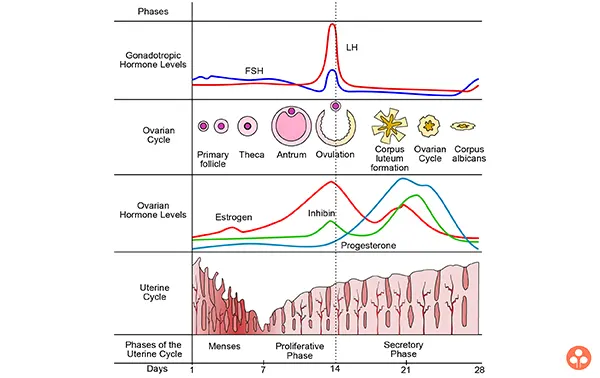
Phases of menstrual Cylae:
- The menstrual cycle consists of following phases:
- Bleeding or menstrual phase:
- It is the first stage of menstrual cycle.
- Its duration is of 5 days but normally bleeding is found for 2 - 3 days.
- In this stage hormones oestrogen, progesterone, follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone are found in minimum quantity
- Total 100 ml, of blood flows in a complete bleeding phase.
- Proliferative phase:
- In this phase F.S.H stimulates development and maturation of graffian follicles.
- In this phase oestrogen level rises which leads to formation of new endometrium.
- It lasts for about 10 - 14 days. Thinnest endometrium is found in this phase.
- It is also called as follicular phase.
- Ovulation phase:
- At this phase ovulation occurs.
- Ovulation occurs in the presence of FSH and LH.
- Thickest endometrium found in this stage.
- It also lasts for about 14 days.
- Secretory phase: In this stage both oestrogen and progesterone levels are high.
- If fertilisation takes place, this stage extends till to the parturition (giving birth to a child).
- If fertilisation does not take place, this stage completes on 28th day of menstrual cycle.
- The commencement of menstruation at puberty is called as menarche.
- It's stoppage around the age of 50 years is called as menopause.
- The period between menarche and menopause is the reproductive phase in human female.
Oogenesis: Oogenesis is a process of formation of ovum. The ovum is a rounded, non-motile cell. Its size varies in different animals depending upon the amount of yolk in it. Ovum consists of two types of coverings:
- Inner thin, transparent, non-cellular covering called as zona pellucida. It is composed of protein and sugars. It is secreted by follicle cells.
- Outer thick covering is called as corona radiata.
Fertilisation: Involves the fusion of haploid male and female gametes to form diploid zygote.
- Three days is required for an ovum to travel down the oviducts to the uterus. An oocyte lives, however only about 24 hours after its liberation from the follicle.
- During copulation the continued stimulation of the glans penis triggers the spasm of muscles of the genital organs creating the orgasm and resulting in the discharge of semen from the urethra.
- When semen is deposited within the vagina, the spermatozoa are deposited high up in the vagina close to the cervix. Spermatozoa remain viable in the female genital tract for 24–72 h.
- The sperms tend to move in all directions, but many find their way up the cervix of the uterus. They reach the top of the fallopian tube within 5 mm of their release due to contractions in the walls of uterus and fallopian tube where they meet the descending ovum.
- When sperm reches in the oviduct, near the ovum then it releases enzymes to dissolve the egg membrane. Now, the sperm nucleus enters in the egg nucleus to form zygote. This fusion of male and female gametes is known as fertilisation. The zygote is formed if copulation has taken place during ovulatory period (middle of menstrual cycle). Fertilisation is marked by the absence of menstrual flow.
Human Population
Human population growth is supported by life capacity of the environment. Life supporting capacity of environment has been increased many fold by advancements made in science and technology like mechanization of agriculture, use of disease free hybrid and high yielding varieties of seeds and use of fertilizers and pesticides etc. The major causes that have contributed towards increase in the human population are : Decline in death rate, control of diseases, decrease in infant mortality, better sanitation and community health schemes and lastly better means of transport.
Not only these, there are many other socio-economic reasons (e.g. signs of national strength, religious and economic beliefs; signs of security in old age; more earning hands in family etc. that have led to an increase in the human population.
Method of control of overpopulation
Education : People, particularly those in reproductive age group, should be educated about the advantages of a small family and ill-effects of large families and overpopulation. In this, mass media like radio, television, newspapers, magazines, posters etc. and educational institutions can play important role. Government should provide free and compulsory primary education to the children below the age of 14 years. In China, there is a legislation making “basic primary education free, compulsory and universal.”
Age of marriage : should be raised. Demographers explain that postponment of female marriage age from 18 years to 20 or 22 years would bring down the birth rate by 20 to 30%. Even a years postponment in each age group will decrease total fertility rate much less than the present 3.5% for the country. But according to an ICMR report, about 49% women in India are married before the legal age of 18 years.
Population Control
The prevention of pregnancy in a woman is called contraception. Any device or chemical which prevents pregnancy is called a contraceptive. All the birth control methods are divided into:
- Barrier methods
- Chemical methods
- Intra uterine contraceptive device (IUCD)
- Surgical methods
Barrier methods:
These are the physical devices to prevent the entry of sperm so that it does not reach the egg. e.g. condoms which can be used to cover the penis. Coverings like diaphragm worn in the vagina can serve the same purpose. Barrier methods also protect against STD’s (sexually transmitted disease).
Chemical methods:
- Oral pills: They are hormonal preparations. They act by changing the hormonal balance of the body, so that eggs are not released & fertilization cannot occur. They are taken orally, therefore commonly called oral contraceptives (OC). These pills can cause side effects.
- Vaginal pills: They contain spermicides and therefore they kill the sperms.
Intra-uterine contraceptive device (IUCD):
They are contraceptives such as a loop or the copper-T placed in the uterus. They prevent implantation in the uterus. They can cause side effects due to irritation of the uterus.
Surgical methods:
- Vasectomy: In males, a small portion of vas deferens (sperm duct) is cut and the cut ends are then ligated (tied). This prevents the sperms from coming out.
- Tubectomy: In females, a small portion of fallopian tubes is cut & the cut ends are then ligated (tied). This prevents the egg to enter the fallopian tube.
Surgical methods are the permanent methods of contraception.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (Stds)
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDS) are those infectious and communicable diseases which are transmitted from an infected person to a healthy but susceptible person during unprotected vaginal, anal and oral sexual contact. These are generally acquired diseases and usually affect the reproductive system of the person but may spread to other body parts as well.
Increasing resistance in the pathogens to antibiotics. So STDS are easier to avoid than to treat and cure. Absitence, monogamy and the use of condoms are the best ways to avoid STD infections. STDS are also called international diseases.
- Gonorrhoea (bacterial disease)
- Syphilis (bacterial disease)
- Warts (viral infection)
- AIDS (viral infection)
AIDS:
It is caused by HIV- Human immuno deficiency virus. This disease weakens the body’s immune system so that body becomes weak & cannot protect itself against infection.
Causes : Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS or aids) is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus, or HIV.
Epidemiology
- It is a sexually transmitted diseases as it can pass from one person to another during sexual intercourse.
- HIV gradually reduces the efficiency of the human immune system, it destroys the body’s ability to fight diseases. This makes the body vulnerable to other life-threatening diseases that finally cause the patients’s death.
- Once a person is infected, the virus remains in the body life-long. Since HIV infection can take many years to manifest itself, the carrier (who is symptomless) can infect other persons for years.
- HIV attacks the helper T-lymphocytes (or T4 cells–a type of leucocyte). The body is unable to fight infections.
- The patient easily catches infections such as pneumonia and often develops various forms of cancer.
- Incubation period is uncertain, varying from a few months to 10-12 years.
Symptoms
- Short flu-like illness. Chronic diarrhoea and severe weight loss.
- Swollen lymph nodes. Decreased count of blood platelets causing blood loss.
- Development of a disfiguring form of skin cancer (Kaposi’s sarcoma). Sweating at night.
- Severe damage to brain, leading to loss of memory and ability to think and speak.
- Due to breakdown of immune system, the victim becomes susceptible to other infections.
Transmission
- The disease is transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person through :
- Sexual contact and infected blood contact, (blood transfusion) are common means of transmission.
- Use of contaminated needles, syringes, blades or razors.
- Through cuts and wounds during close contact between infected and non-infected people.
- From infected mother to foetus through placenta and through breast feeding.
- Homosexual relationship and sharing of needles for drug abuse are high risk groups
Gonorrhoea:
Cause :It is a bacterial (gram negative) and veneral (sexually transmitted) disease caused by a diplococcus bacterium, Neisseria gonorrhoea.
Epidemiology :It is a sexually transmitted disease spread by sexual contact with infected persons. The risk of infection depends upon number of exposures.
Incubation period :About 2 to 10 days.
Symptoms :Gonorrhoea is characterised by inflammation of mucous membrane of urinogenital tract so the patient feels burning sensation during urination. The symptoms are more obvious in males than in females. It may also cause arthritis, female sterility and gonococcalophthalmia (eye infection in the children – also called ophthalmia neonatorum when contact during its passage through the birth canal).
Prophylaxis :Avoiding prostitution and homosexuality. Identifying the asymptomatic individuals which form high risk group. Health education and use of condoms.
Therapy :Recommended antibiotics are ceftriaxone (most effective), ampicillin and penicillin.
How Do Organisms Reproduce ?
- Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms (offspring) are produced from their parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life. Each individual organism exists as the result of reproduction.
- The inheritance of features from parents can be transferred to their offsprings through chromosomes present in the nucleus of the cell.
- Basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy.
- Some changes in DNA copying produces variations in organisms known as mutations.
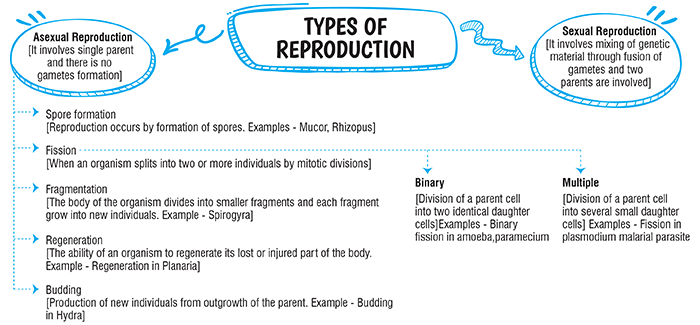
- Vegetative propagation in plants is also an example of asexual reproduction. New plants can be grown from different vegetative parts of the plants like roots, stems, leaves etc.
- Some plants like Bryophyllum develops adventitious buds on their leaves which develops into new plants.
- Modified tuberous roots like sweet potato can be propagated vegetatively when planted in soil.
- Artificial methods of vegetative propagation includes cutting, layering, grafting etc.
- The parts of a flower are calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium.
- Calyx is the outermost whorl of a flower which is a collection of sepals mostly green in colour and they are protective in function.
- Corolla is the collection of petals, they are brightly coloured and helps in attraction of insects for pollination.
- Androecium is a collection of stamens which are the male reproductive organs of a flower. A stamen consists of anther and filament. Anther contains pollen sacs in which pollen grains are produced. Pollen grains contain male gametes.
- Gynoecium is a collection of carpels which are the female reproductive organs of a flower.
- A carpel consists of stigma, style and ovary
- The ovary contains ovules which contains the female gametes.
- Double fertilisation is a complex fertilisation mechanism in flowering plants. This process involves the fusion of a female gametophyte (megagametophyte, also called the embryo sac) with two male gametes (sperm).
- Ovules grow into seeds and ovaries grow into fruits after fertilisation.
- Gonads are primary sex organs in humans. Testes are male gonads which produces sperms whereas ovaries are female gonads which produce eggs.
- Testes are found within sac like structures called scrotum. Vas deferens or sperm ducts carry sperms from testis.
- Ovaries produce eggs. The fertilisation of egg with sperms occurs at oviduct. After fertilisation zygote is formed which develops into embryo that grows in uterus to a full term baby in about 280 days which is called gestation period.
- If fertilisation does not occur the egg disintegrates and along with blood and mucus it comes out through the vagina. This cycle occurs every month in females known as menstrual cycle.
- To avoid rapid growth of population some preventive measures are taken which is called birth control.
- The infectious diseases which spread from an infected person to healthy ones through sexual contact are called Sexually Transmitted Diseases or STDs. Examples are AIDS, syphilis, gonorrhea.
| 1. Asexual reproduction: The process of producing offsprings which involves a single parent without the formation of gametes is called asexual reproduction. | 8. Primary sex organs: They are the gonads i.e., testes and ovaries which produce gametes and secrete sex hormones. |
| 2. Spore: A spore is a single-celled or multi-celled reproductive structure which gets separated from its parent and under the favourable conditions gives rise to a new individual. | 9. Gametes: The special cells involved in sexual reproduction to produce the offsprings are called gametes or sex cells. |
| 3. Seed: A seed is the reproductive unit of a plant from which a new plant grows. | 10. Puberty: The age at which sex hormones are produced, reproductive organs become matured and have the capacity to give rise to new individuals and there is development of secondary sexual characters in both males and females. |
| 4. Vegetative propagation: It is mainly seen in plants and is an asexual mode of reproduction where a new plant grows from different parts of plant like roots, stem, leaves etc., rather than from a seed. | 11. Fertilisation: The process of fusion of male and female gametes to produce the zygote is called fertilisation. |
| 5. Tissue culture: The production of new plants from a small piece of plant tissues or cells removed from the growing tips of a plant in a suitable growth medium is called tissue culture. | 12. Gestation period: It is the time from fertilisation till the birth of the new born. |
| 6. Pollination: The process of transfer of pollen grains from anthers of stamens to the stigma of carpel within the same flower or different flower of same plant or to any other flowers of different plants but of same species is called pollination. | 13. Parturition: The delivery of full term baby from the uterus of mother after the end of gestation period is called parturition. |
| 7. Double fertilisation: The process by which a male gamete fuses with an egg to form zygote and the second male gamete unites with two polar nuclei to form endosperm is called double fertilisation. | |