Carbon And Its Compounds Class 10 Notes Chemistry Science
Chapter 4
To download the complete Syllabus (PDF File), Please fill & submit the form below.
Introduction
Carbon (non-metal) Latin word Carbon = Coal Earth crust has only 0.02% carbon in the form of minerals. (Like carbonates, hydrogen carbonates, coal and petroleum), and the atmosphere has 0.03% of carbon dioxide. In the present chapter, we shall study the characteristics of this element and also about the nature of bonding in which it participates.Organic compounds
The compounds containing Carbon and Hydrogen which are obtained from Plants or Animals and now-a-days which can also be synthesized in the laboratory. Example - CH4, CHCl3. The study of organic compounds is called Organic Chemistry. There are more than 7 million compounds of Carbon known. Hundreds of new compounds are discovered or made artificially each year. Compounds of carbon alone outnumber, total of all the compounds of the rest of the elements put together.Carbon
Symbol
Atomic number
Electronic configuration
Valency
Tendency
Type of bonds
C
6
(2, 4)
4
to share its four valence electrons
covalent bond

- For attaining stability Carbon must either lose 4 electrons or gain 4 electrons or share 4 electrons from its outermost If it were to Gain or Lose electrons -
- It can Gain 4 electrons to form C4 - ions.
But it would be difficult for the nucleus with 6 protons, to hold on to 10 electrons i.e. 4 extra electrons. - It can lose 4 electrons to form a C4+
But it would require a large amount of energy to remove 4 electrons leaving
- It can Gain 4 electrons to form C4 - ions.
Carbon overcomes this problem by Sharing these 4 electrons with other carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements. The shared electrons belong to the outermost shell of both the combining atoms. Thus, both the combining atoms attains stability by acquiring the Noble gas configuration.
Versatile nature of Carbon
Carbon has the following properties due to which it is able to form Million of compounds :
- Tendency to form covalent bond - Carbon has four electrons in its valence shell. It shows the tendency tshare these four electrons with four different atoms like four Hydrogen by forming four covalent bonds.
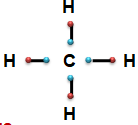
- Small atomic size - Carbon atom has comparatively
small size, i.e., its atomic radius is smaller. Hence, the valence shell in the carbon atom is comparatively nearer. Therefore, the shared pair/ pairs of electrons are comparatively, nearer to the positively charged nucleus.
Hence, held very tightly, i.e., bonds are strong. - Catenation - The property of direct bonding between the atoms of the same elements to form chains of that element is called Catenation. These chains can be straight chains ,branched chains or cyclic chains of various shapes and sizes.
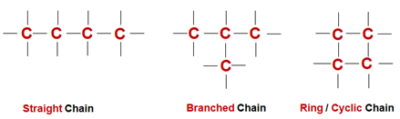
- Tendency to form multiple bonds - Carbon not only forms single covalent bonds with itself or other elements but also forms multiple bonds i.e. Double or Triple bond with itself and other compounds.

Allotropes of Carbon
- The property due to which an element exists in two or more physical forms is called Allotropy.
- The different physical forms of an element are called Allotropes.
Carbon has the unique property of existing in different forms such as diamond, Graphite, Coke, Charcoal, Lampblack and gas carbon. Allotropes have different physical properties (Due to different arrangement of atoms in them but have the same chemical properties).
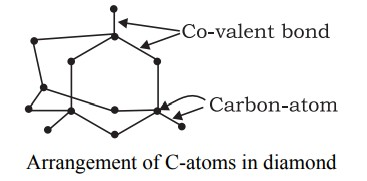
- Diamond - In Diamond , each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms, by four single covalent bonds, forming a rigid, three – dimensional, closely packed, structure. This results in Higher density of Diamond (than Graphite). All valence electrons used in bonding, Hence, no Free electrons - No electrical conductivity
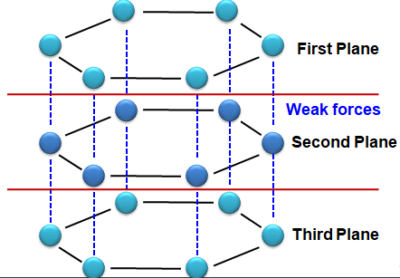
- Graphite - In Graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other Carbon atoms in the same plane giving a hexagonal array (arrangement). One electron on each carbon atom is free (Not used in bonding). Hence, Graphite is a good conductor of electricity. Graphite structure is formed by the hexagonal array being Placed in layers one above the other, bonded by weak forces (Van der Waals Forces), hence the layers can slip above one another.
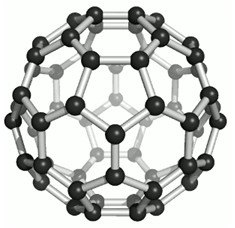
- Fullerenes - First one to be identified was C-60 which has carbon atoms arranged in the shape of a football. Since this looked like the geodesic dome designed by the US Architect Buck Minster Fuller, the Molecule was named Fullerene. Bucky Balls (C-60) were discovered in soot. They are as soft as Graphite. It consists of 20 Hexagons and 12 Pentagons. This was nicknamed as ‘Bulky Ball’.
Hydrocarbons
The compounds containing carbon and hydrogen elements only, are called Hydrocarbons.

Types of hydrocarbons :
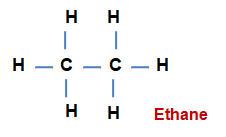
Saturated hydrocarbon 一 The hydrocarbons in which all the four valencies of a carbon atom in a molecule are satisfied by four different atoms, are called as Saturated hydrocarbons.
General formula CnH2n+2 ; n = 1, 2, 3....
n = 1 CH4 methane
n = 2 C2H4 ethan
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 一 The hydrocarbons in which all the four valencies of a carbon atom in a molecule are not satisfied by four different atoms , are called as Unsaturated Hydrocarbons.
These are two types:
a) Alkenes : General formula CnH2n ; n = 2, ...
n = 2 C2H4 ethene
n = 3 C3H6 propene
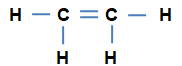
b) Alkyne : General formula CnH2n-2 ; n = 2, ...
n = 2 C2H2 ethyne
n = 3 C3H4 propyne
![]()
- Alkyl group 一 The group formed by the removal of one hydrogen atom from alkane molecule, is called as Alkyl Group. The name of alkyl group is written by replacing the suffix – ane of alkane by 一yl
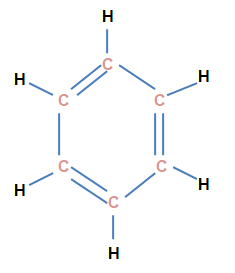
- Aromatic hydrocarbons 一 The unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one ring of 6 - carbon joined alternately by single and double bonds, are called as Aromatic hydrocarbons.
Isomerism
Organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae, are known as Isomers. The existence of two or more compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formulae is called Isomerism.
Example - Structural Isomers of Butane

Structural Isomers of Pentane

Homologous series
Organic Compounds having the same General Molecular Formula, Similar structure and Similar Chemical Properties, placed together in the same group are called Homolog, and the series of such similar compounds is called Homologous series. Characteristics of homologous series- All the members of a homologous series have the same general molecular formula.
- The difference in molecular formulae between any two adjacent members of a homologous series is CH2.
- The difference in molecular mass between any two adjacent members of a homologous series is 14.
- The methods of preparation and chemical properties of any member of the series are similar.
- The physical properties such as melting point, boiling point in a homologous series changes gradually as we go down the series.

IUPAC nomenclature
- Longest Continuous Chain : Select the longest chain in a carbon compound. This chain is the Parent chain and gives name to the Parent Hydrocarbon. Longest chain may or may not be a straight chain but it should be continuous.
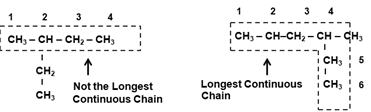
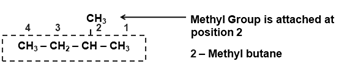
- Naming the Side Chain : Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain as 1 , 2 , 3 , ……..etc. starting from the end which gives lower number to the carbon atoms carrying the Substituents (Alkyl Group) that is Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain as 1 , 2 , 3 , ……..etc. from the end which has the substitution nearest to it.

However, If there are two or more Substituents attached to the Parent chain, then, The end of the parent chain which gives lowest sum of the numbers is selected for numbering.
- The position of each substituent is designated by the number of the carbon atom to which it is attached.
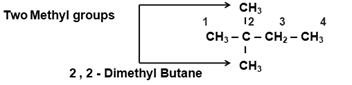
- In case of two or more substituents : Use prefix di - (for two), tri- (for three), tetra- (for four) etc before the name of substituent.
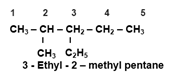
- If the compound contains different Alkyl Groups, they are named in the Alphabetical Order. (Ethyl before Methyl).
Chemical properties of carbon compounds
- Combustion reaction : On burning alkanes, in excess of air, carbon-dioxide and water vapor is formed with evolution of heat.
CH4 + 2O2 ⟶ CO2 + 2H2O + Heat - Oxidation reaction : The substances capable of adding oxygen to other substances are known as oxidizing agents. Alkaline Potassium Permanganate (Violet) or Acidified Potassium Dichromate (Orange) oxidizes, Alcohols to Acids.
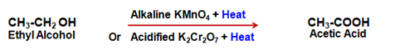
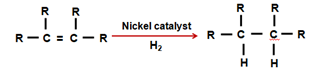
- Addition reaction : Unsaturated hydrocarbons add Hydrogen in presence of catalysts like Palladium or Nickel to produce saturated Hydrocarbons.
Hydrogenation of oils - The unsaturated oils get converted to saturated fats, thereby leading to Solidification. It is commonly used in the Hydrogenation of vegetable oils using nickel as Catalyst, to produce ‘Vanaspati Ghee’.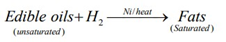
- Substitution reaction : Alkanes undergo substitution reactions on reaction with Halogens. In presence of UV light and excess of halogen, Chlorine gets added to hydrocarbons very quickly.
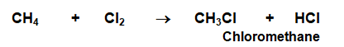
Ethanol (C2 H5OH)
Ethanol is commonly called Alcohol. Its common name is ethyl alcohol.
- Rectified spirit - A solution containing 95% Alcohol and 5 % Water is called Rectified Spirit.
- Absolute alcohol - Completely pure or 100 % alcohol is called Absolute Alcohol.
Physical properties of ethanol
- Colourless liquid
- Pleasant smell and a burning taste.
- Volatile liquid
- Boiling point 78ºC
- Soluble in water (intermolecular hydrogen bonding).
- It has no effect on any litmus solution.
Chemical properties of ethanol
- Combustion Reaction
CH3CH2OH + 3O2 ⟶ 2CO2 + 3H2O
It is a highly inflammable liquid. - Reaction with Sodium
2C2H5OH + 2Na ⟶ C2H5O–Na+ + H2(↑) - Reaction to give unsaturated hydrocarbon - Heating Ethanol, at 443 K with excess of concentrated Sulphuric Acid, results in the Dehydration of Ethanol to give Ethene/Ethylene .
$$CH_3 \space CH_2\space OH\xrightarrow[H_2SO_4]{Hot\space Conc.} CH_2=CH_2+H_2O$$
This reaction is called Acidic Dehydration. - Reaction with Ethanoic Acid or Acetic Acid - Ethanol reacts with Ethanoic acid or Acetic Acid in presence of concentrated Sulphuric acid to form Ethyl Ethanoate or Ethyl Acetate (Ester). This reaction is called the Esterification reaction. Compounds having the formula R–COO–R’ are called Esters.

Uses of esters are in making perfumes and flavouring agents for ice creams.
Uses of ethanol
- As an antifreeze in automobile radiators.
- As a preservative for biological specimens.
- As an antiseptic to sterilize wounds in hospitals.
- As a solvent for drugs, oils, fats, perfumes, dyes, etc.
- In the preparation of methylated spirit (mixture of 95% of ethanol and 5% of methanol),rectified spirit (mixture of 95.5% of ethanol and 4.5% of water, Power alcohol (mixture of petrol and ethanol) and denatured spirit (Ethanol mixed with Pyridine).
- In Cough and Digestive syrups.
Denatured alcohol and its harmful effects
Alcohol is denatured by adding methanol, pyridine, copper sulphate. Harmful effects of drinking denatured alcohol are as follows -
- If ethanol is consumed, it tends to slow down metabolism of our body and depresses the central nervous system.
- It causes mental depression and emotional disorder.
- It affects our health by causing ulcer, high blood pressure, cancer, brain and liver damage.
- Nearly 40% of accidents are due to drunken driving.
- Unlike ethanol, intake of methanol in very small quantities can cause death.
- Methanol is oxidized to methanal (formaldehyde) in the liver and methanol reacts rapidly with the components of cells.
- Methanol also affects the optic nerve, causing blindness.
Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)
Ethanoic acid is most commonly known as acetic acid and belongs to a group of acids called carboxylic acids.
Preparation of Ethanoic acid
$$CH_3 \space CH_2\space OH\xrightarrow[Alk.KMnO_4/Acid.K_2Cr_2O7]{Oxidation} CH_3COOH+H_2O$$
Physical Properties of Ethanoic acid
- Ethanoic acid is a colourless liquid and has a sour taste.
- Ethanoic acid is miscible with water in all proportions.
- Boiling point (391 K), of Ethanoic Acid, is higher than corresponding alcohols, aldehydes and Ketones.
- On cooling, pure Ethanoic acid is frozen to form ice like flakes.
Chemical properties of ethanoic acid
- Esterification reaction - Ethanoic Acid reacts with absolute alcohol in presence of an acid catalyst to produce an Ester.
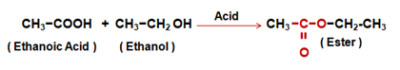
- Saponification reaction - Esters react in the presence of an acid or a Base to give back the Alcohol and Sodium Ethanoate. This reaction is called Saponification.
$$CH_3-COO-C_2H_5\xrightarrow[]{NaOH} CH_3-COONa+CH_3=CH_2\space OH$$ - Reaction with a base - Like mineral acids , Ethanoic Acid reacts with a base like Sodium Hydroxide to produce a salt like Sodium Ethanoate (Sodium Acetate) and Water.

- Reaction with Carbonates and Hydrogen Carbonates : Ethanoic Acid reacts with Carbonates and Bicarbonates to produce salt, Carbon dioxide and Water. The salt produced is Sodium Acetate.
2CH3-COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3-COONa + H2O+CO2
Uses of ethanoic acid
- For making vinegar which is used as a preservative in food and fruit juices.
- 5–8 % solution of Acetic Acid in water is called Vinegar.
- As a laboratory reagent.
- In the preparation of dyes, perfumes and medicine.
| Ethyl alcohol | Acetic Acid | |
|
Blue litmus solution remain unaffected. | Blue litmus solution change to red colour. |
|
No effervescen | CH2COOH+NaHCO3 → CH3COO-Na+ H2O + CO Brisk effervescence of Co2 |
Soaps and detergents
Soaps are Sodium or Potassium salts of long chain fatty acids, with formula R − COOH. Soaps have a general molecular formula of R − COONa/K.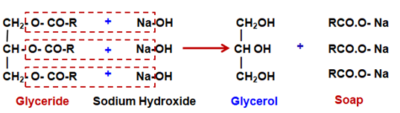
As the reaction leads to the formation of soap, it is called the Saponification reaction.
Hardness of Water : Hardness of water is due to Bicarbonates, Chlorides and Sulphates - Salts of Ca++ and Mg++ present in hard water. 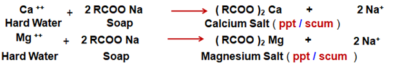
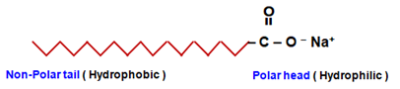
Structure of Soaps : Soaps consists of two parts :
- A long hydrocarbon chain which is water repelling (called Hydrophobic). It is called a nonpolar tail.
- An ionic part which is water attracting (called Hydrophilic). It is called the polar head.
Synthetic Detergents are the sodium salts of Sulphonic acids.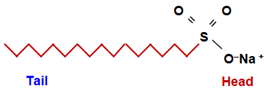
Cleansing action of soap - Soaps and detergents dissociate in solution to form carboxylate ions (RCOO-) or sulphonate ions (RSO3 ) and the cations (Na ). The alkyl component of the carboxylate ion, which carries a lengthy chain of hydrocarbons, is the tail pointing towards the oil droplets, while the COO_ portion is the head heading towards _ water. It is the SO3 part of a detergent that points towards water. The image clearly shows this, with the solid circles (•) representing the polar groups and the
wavy lines ( ~ ) representing the alkyl parts. Micelle is the name given to this type of structure. By serving as a bridge between the two, soaps or detergent aid in the formation of a stable emulsion of oil and water. The oil droplets and dirt particles separate from the surface. The oil droplets, together with dirt particles, separate from the fibers of the garments and enter the emulsion. As a result, the clothing is free of dust and filth.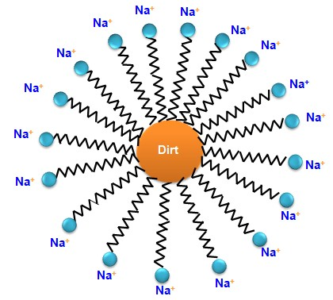
- Detergents, unlike soap, do not react with the magnesium and calcium salts found in hard water to form scum. They are more efficient cleaners than soap. However, Detergents can be very harsh on skin / hair for humans.
- Soaps are made from natural fats and oils and so are fully Soaps do not wash well in hard water and do not form much lather or foam. The calcium, magnesium or iron ions of hard water form an insoluble sticky grey coloured precipitate called scum, which restricts the cleansing action of soap and makes washing more difficult. The scum formed also hardens and de-colours the fabric.
- Detergents are made from synthetic chemicals. These chemicals do not break down in the environment, and so they cause huge amounts of pollution in our waterways- killing fish and water plants.
| 1. Hydrocarbons: An organic compound containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms. | 9. Homologous series: A homologous series is a group of organic chemical compounds, usually listed in order of increasing size, that have a similar structure (and hence also similar properties) and whose structures differ only by the number of CH2 units in the main carbon chain. |
| 2. Allotropy: The phenomenon of existence of two or more different physical forms of a chemical element. | 10. Esterification: The chemical reaction that takes place during the formation of an ester is called esterification. Ester is obtained by an esterification reaction of an alcohol with carboxylic acid. |
| 3. Catenation: The property of self linking of elements to form a long chains of compounds. | 11. Saponification: A chemical reaction in which an ester is heated with an alkali to make soap. |
| 4. Tetravalency: Tetravalency is the state of an atom in which there are four electrons available with the atom for covalent chemical bonding. | 12. Soaps: Soaps are sodium and potassium salts of long chain of fatty acids such as stearic acid, palmitic acid etc. |
| 5. Saturated hydrocarbons: A substance in which the atoms are linked by single bonds. | 13. Detergents: They are ammonium or sulphonate salts of long chain hydrocarbons. |
| 6. Unsaturated hydrocarbons: A substance in which atoms are linked by double or triple bond. | 14. Hydrophobic substance: “Water fearing”. Hydrophobic compounds do not dissolve easily in water, and are usually non-polar. |
| 7. Isomers: Compounds having similar molecular formula but different structure are known as Isomers. | 15. Hydrophilic substance: Having an affinity for water; capable of interacting with water through hydrogen bonding. |
| 8. Isomerism: The phenomenon in which the compounds have the same molecular formula and different structural formula is known as Isomerism. | |
